Degranulation of mast cells
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mast cells are cells of hematopoietic origin which have gained notoriety over the years for their role as central players in atopic disorders and anaphylaxis. Indeed, it has been in this context that much of the research in this field has degranulation of mast cells conducted.
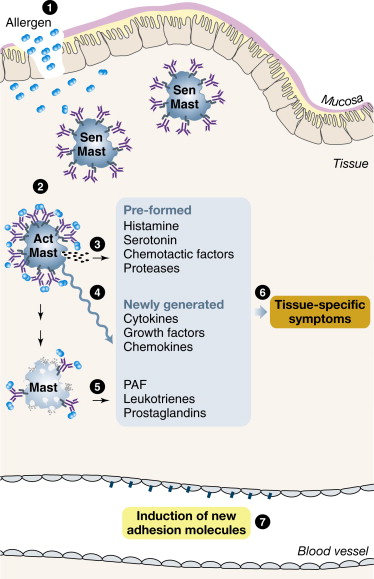
This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse this site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Review our cookies information for more details. Mast cells are allergy cells responsible for immediate allergic reactions. In allergic reactions, this release occurs when the allergy antibody IgE , which is present on the mast cell surfaces, binds to proteins that cause allergies, called allergens. This triggering is called activation, and the release of these mediators is called degranulation.
Degranulation of mast cells
A mast cell also known as a mastocyte or a labrocyte [1] is a resident cell of connective tissue that contains many granules rich in histamine and heparin. Specifically, it is a type of granulocyte derived from the myeloid stem cell that is a part of the immune and neuroimmune systems. Mast cells were discovered by Paul Ehrlich in The mast cell is very similar in both appearance and function to the basophil , another type of white blood cell. Although mast cells were once thought to be tissue-resident basophils, it has been shown that the two cells develop from different hematopoietic lineages and thus cannot be the same cells. Mast cells are very similar to basophil granulocytes a class of white blood cells in blood , in the sense that both are granulated cells that contain histamine and heparin , an anticoagulant. Their nuclei differ in that the basophil nucleus is lobated while the mast cell nucleus is round. The Fc region of immunoglobulin E IgE becomes bound to mast cells and basophils, and when IgE's paratopes bind to an antigen, it causes the cells to release histamine and other inflammatory mediators. Furthermore, they share a common precursor in bone marrow expressing the CD34 molecule. Basophils leave the bone marrow already mature, whereas the mast cell circulates in an immature form, only maturing once in a tissue site. The site an immature mast cell settles in probably determines its precise characteristics. Mast cells in rodents are classically divided into two subtypes: connective tissue -type mast cells and mucosal mast cells. The activities of the latter are dependent on T-cells. Mast cells are present in most tissues characteristically surrounding blood vessels, nerves and lymphatic vessels, [11] and are especially prominent near the boundaries between the outside world and the internal milieu, such as the skin , mucosa of the lungs , and digestive tract , as well as the mouth , conjunctiva , and nose. Mast cells play a key role in the inflammatory process.
DVM Program. Petersen-Jones Laboratory.
Degranulation is a cellular process that releases antimicrobial cytotoxic or other molecules from secretory vesicles called granules found inside some cells. It is used by several different cells involved in the immune system , including granulocytes neutrophils , basophils , eosinophils , and mast cells. It is also used by certain lymphocytes such as natural killer NK cells and cytotoxic T cells , whose main purpose is to destroy invading microorganisms. Degranulation in mast cells is part of an inflammatory response, and substances such as histamine are released. Granules from mast cells mediate processes such as "vasodilation, vascular homeostasis, innate and adaptive immune responses, angiogenesis, and venom detoxification. Antigens interact with IgE molecules already bound to high affinity Fc receptors on the surface of mast cells to induce degranulation, via the activation of tyrosine kinases within the cell.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Mast cells are immune cells of the myeloid lineage and are present in connective tissues throughout the body. The activation and degranulation of mast cells significantly modulates many aspects of physiological and pathological conditions in various settings. With respect to normal physiological functions, mast cells are known to regulate vasodilation, vascular homeostasis, innate and adaptive immune responses, angiogenesis, and venom detoxification. On the other hand, mast cells have also been implicated in the pathophysiology of many diseases, including allergy, asthma, anaphylaxis, gastrointestinal disorders, many types of malignancies, and cardiovascular diseases. This review summarizes the current understanding of the role of mast cells in many pathophysiological conditions. Mast cells are important cells of the immune system and are of the hematopoietic lineage. Mast cells are originated from pluripotent progenitor cells of the bone marrow, and mature under the influence of the c-kit ligand and stem cell factor in the presence of other distinct growth factors provided by the microenvironment of the tissue where they are destined to reside. Under normal conditions, mature mast cells do not circulate in the bloodstream.
Degranulation of mast cells
Your dog is restless and anxious, and suddenly chewing and scratching at his red, irritated mast cell tumor. Is he having a degranulation event? Mast cell tumors are fairly common in dogs. These tumors develop from mast cells, a type of immune cell that contains little packets or granules of histamine and other chemicals.
Lcm for 7 and 9
Career Resources Expand. International Visa Options. Mast Cells, Angiogenesis and Cancer. By continuing to browse this site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies. Genetic Eye Screening. Once these criteria are met, further testing should rule out primary clonal mast cell disorders that can also cause these symptoms. Hussey Laboratory. Furthermore, they share a common precursor in bone marrow expressing the CD34 molecule. In a person who has encountered an allergen, mast cell degranulation the release of histamine would initiate mucus production, redness, inflammation, itchiness, and other signs and symptoms typical of allergic reactions. Omalizumab which blocks binding of IgE to its receptors has been reported to reduce mast cell reactivity and sensitivity to activation which can reduce anaphylactic episodes.
New therapeutic tools may be on the horizon for patients with allergies, IBS, migraines, and other immune-triggered conditions.
The understanding of mast cell biology has dramatically increased over the past two decades, largely due to three major developments. ISSN In fact, a recent review indicated that peripheral inflammatory stimuli can cause microglia activation [51], thus possibly involving MCs outside the brain. Welcome Information. Allergy Proc. The Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology. GOAL 1. DVM Class Composition. Work For Us. Instinct: Electronic Medical Records System. Equine Services. MS Degree Guidelines. Contents move to sidebar hide. Taking the Next Step. Ganey Laboratory.

It is simply excellent phrase
It is remarkable, it is an amusing phrase
Completely I share your opinion. In it something is also to me this idea is pleasant, I completely with you agree.