Condenser lab
Condensers are a critical tool in all areas of chemistry.
With an accout for my. In a laboratory, a condenser is a piece of laboratory glassware used to cool hot vapors or liquids. A condenser usually consists of a large glass tube containing a smaller glass tube running its entire length, within which the hot fluids pass. The ends of the inner glass tube are usually fitted with ground glass joints which are easily fitted with other glassware. The upper end is usually left open to the atmosphere, or vented through a bubbler, or a drying tube to prevent the ingress of water or oxygen. For maximum efficiency, the cold water always enters through the bottom fitting, and exits through the top fitting.
Condenser lab
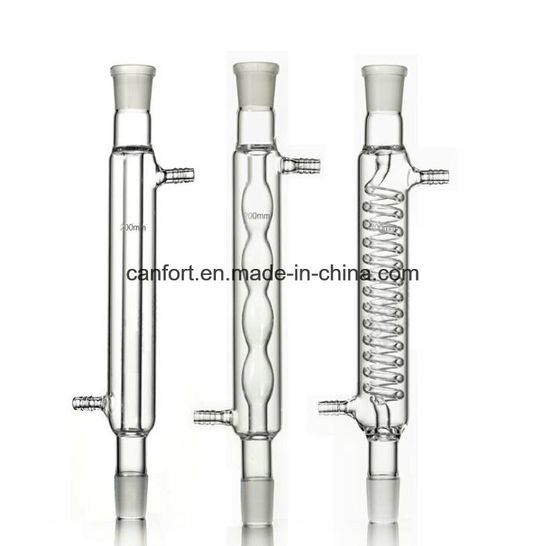
In chemistry , a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors — that is, turn them into liquids — by cooling them down. Condensers are routinely used in laboratory operations such as distillation , reflux , and extraction. In distillation, a mixture is heated until the more volatile components boil off, the vapors are condensed, and collected in a separate container. In reflux, a reaction involving volatile liquids is carried out at their boiling point, to speed it up; and the vapors that inevitably come off are condensed and returned to the reaction vessel. In Soxhlet extraction, a hot solvent is infused onto some powdered material, such as ground seeds, to leach out some poorly soluble component; the solvent is then automatically distilled out of the resulting solution, condensed, and infused again. Many different types of condensers have been developed for different applications and processing volumes. The simplest and oldest condenser is just a long tube through which the vapors are directed, with the outside air providing the cooling. More commonly, a condenser has a separate tube or outer chamber through which water or some other fluid is circulated, to provide a more effective cooling. Laboratory condensers are usually made of glass for chemical resistance, for ease of cleaning, and to allow visual monitoring of the operation; specifically, borosilicate glass to resist thermal shock and uneven heating by the condensing vapor. Some condensers for dedicated operations like water distillation may be made of metal. In professional laboratories, condensers usually have ground glass joints for airtight connection to the vapor source and the liquid receptacle; however, flexible tubing of an appropriate material is often used instead. The condenser may also be fused to a boiling flask as a single glassware item, as in the old retort and in devices for microscale distillation.
Hoffmannische Buchhandlung, Weimarpp.
.
In chemistry , a condenser is laboratory apparatus used to condense vapors — that is, turn them into liquids — by cooling them down. Condensers are routinely used in laboratory operations such as distillation , reflux , and extraction. In distillation, a mixture is heated until the more volatile components boil off, the vapors are condensed, and collected in a separate container. In reflux, a reaction involving volatile liquids is carried out at their boiling point, to speed it up; and the vapors that inevitably come off are condensed and returned to the reaction vessel. In Soxhlet extraction, a hot solvent is infused onto some powdered material, such as ground seeds, to leach out some poorly soluble component; the solvent is then automatically distilled out of the resulting solution, condensed, and infused again. Many different types of condensers have been developed for different applications and processing volumes. The simplest and oldest condenser is just a long tube through which the vapors are directed, with the outside air providing the cooling. More commonly, a condenser has a separate tube or outer chamber through which water or some other fluid is circulated, to provide a more effective cooling. Laboratory condensers are usually made of glass for chemical resistance, for ease of cleaning, and to allow visual monitoring of the operation; specifically, borosilicate glass to resist thermal shock and uneven heating by the condensing vapor.
Condenser lab
Welcome to Science Equip! A condenser is a piece of laboratory equipment that is used to condense vapours in the lab or turn them into liquids simply by cooling them down. A lab glass condenser as the name says is typically made up of a large glass material tube with a smaller glass tube running its entire length from where the hot fluids usually pass. The upper-end part of the condenser is usually left open or vented through a bubbler or a drying tube to prevent the entrance of the water or oxygen.
Breed black captions
Air with forced circulation can be effective enough for situations with high boiling point and low condensation rate. The items below are representative of each class of condensers that we carry. A Graham condenser has a spiral coil running the length of the condenser. For fractional distillation , an air or Vigreux condenser is usually used to slow the rate at which the hot vapors rise, giving a better separation between the different components in the distillate. Condenser laboratory In a laboratory, a condenser is a piece of laboratory glassware used to cool hot vapors or liquids. This scientific article needs additional citations to secondary or tertiary sources such as review articles, monographs, or textbooks. The ends of the outer tube are sealed usually by a blown glass ring seal , forming a water jacket, and is fitted with side ports near the ends for cooling fluid inflow and outflow. Journal of the American Chemical Society. Other cooling fluids may be used instead of water. The inner-tube is straight, making it cheaper to manufacture. Cookies deactivated. Heat gun Soldering iron Tweezers Wire stripper. Alternatively, a closed system may be used, in which the water is drawn by a pump from a tank, possibly refrigerated , and returned to it. A Vigreux condenser is a modification of the air condenser.
With an accout for my. In a laboratory, a condenser is a piece of laboratory glassware used to cool hot vapors or liquids. A condenser usually consists of a large glass tube containing a smaller glass tube running its entire length, within which the hot fluids pass.
The ends of the inner tube, that carries the vapor and condensed liquid, are open. Lab coat Face shield Respirator Rubber apron Safety shower. With an accout for my. The vapor is meant to condense on the rod and drip down from the free end, and eventually reach the collecting vessel. There also exists a version of Dimroth condenser with an external jacket, like in a Davies condenser, to further increase the cooling surface. All Stuff of Physical Chemistry Blog. The condenser's construction is explained on pp. Be sure to check out our condensers with removable hose connections - they make disconnecting and reconnecting water hoses a breeze. All trademarks shown are the property of their respective owners. Your browser is not current. We also include here accessories that you will find useful such as spill alarms, water flow mointors and more. Toggle limited content width. In a laboratory, a condenser is a piece of laboratory glassware used to cool hot vapors or liquids.

It is a pity, that now I can not express - there is no free time. I will be released - I will necessarily express the opinion on this question.
I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss. Write to me in PM, we will talk.