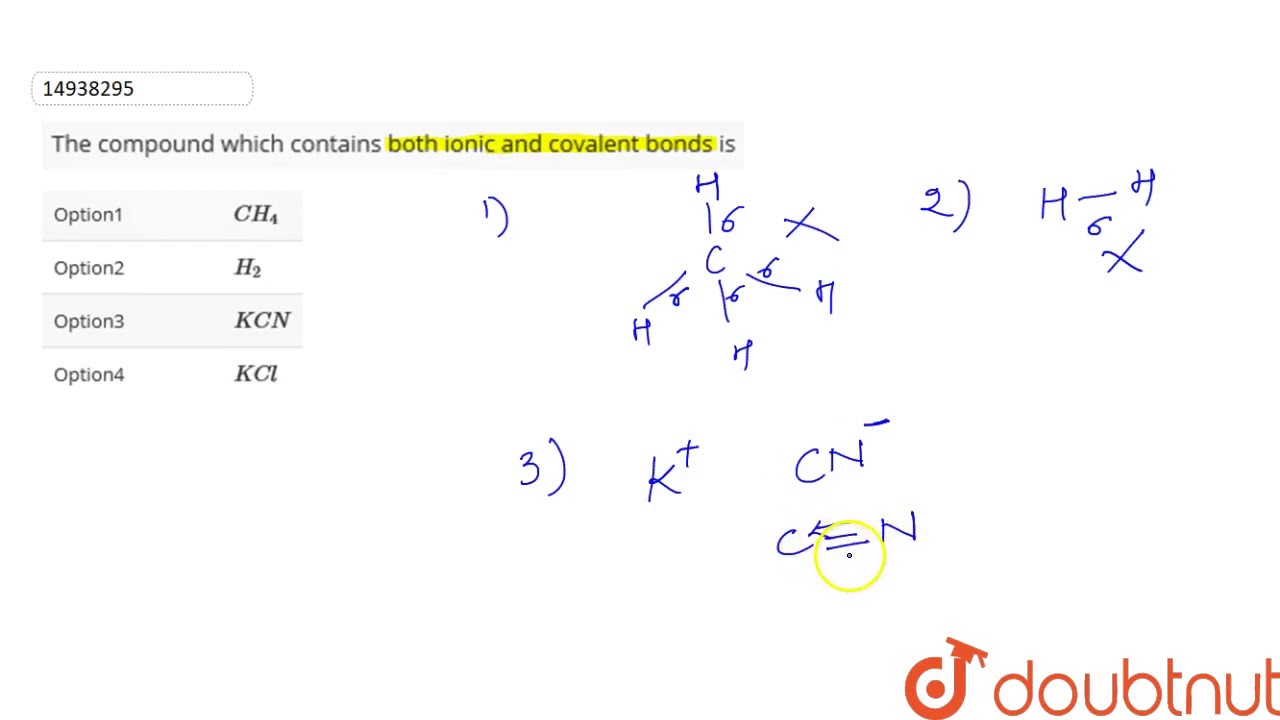
Compound containing both ionic and covalent bonds
An ionic bond is a chemical bond between two atoms in which one atom seems to donate its electron to another atom. Covalent bondson the other hand, appear to involve two atoms sharing electrons reach a more stable electron configuration. These compounds contain polyatomic ions. Many of these compounds contain a metal, a nonmetal, and also hydrogen.
Last updated on Jan 7, Get Started. SSC Exams. Banking Exams. Teaching Exams.
Compound containing both ionic and covalent bonds
Some chemical compounds contain both ionic and covalent bonds. These are ionic compounds that contain polyatomic ions. Often, a compound with both types of bonds contains a metal bonded to an anion of covalently bonded nonmetals. Less often, the cation is polyatomic. Sometimes nonmetals bond to form a cation with enough electronegativity difference from the anion to form an ionic bond! Here are examples of compounds with both ionic and covalent bonds. Remember, an ionic bond occurs when one atom essentially donates a valence electron to another atom. A covalent bond involves atoms sharing electrons. In pure covalent bonds, this sharing is equal. In polar covalent bonds, the electron spends more time with one atom than the other. For example, in potassium cyanide KCN , the carbon C and nitrogen N are both nonmetals, so they share a covalent bond. The potassium atom K is a metal, so it bonds to the nonmetallic anion via an ionic bond. X-ray diffraction of KCN crystals verifies this arrangement. The potassium ions are separate from the bonded carbon and nitrogen ions that form the cyanide anion. Compounds with both ionic and covalent bonds form ionic crystals.
WB Police Sergeant. India Post MTS. Delhi Home Guard.
.
In ordinary chemical reactions, the nucleus of each atom and thus the identity of the element remains unchanged. Electrons, however, can be added to atoms by transfer from other atoms, lost by transfer to other atoms, or shared with other atoms. The transfer and sharing of electrons among atoms govern the chemistry of the elements. During the formation of some compounds, atoms gain or lose electrons, and form electrically charged particles called ions Figure 2. You can use the periodic table to predict whether an atom will form an anion or a cation, and you can often predict the charge of the resulting ion. Atoms of many main-group metals lose enough electrons to leave them with the same number of electrons as an atom of the preceding noble gas. For example, a neutral calcium atom, with 20 protons and 20 electrons, readily loses two electrons. When atoms of nonmetal elements form ions, they generally gain enough electrons to give them the same number of electrons as an atom of the next noble gas in the periodic table. For example, the neutral bromine atom, with 35 protons and 35 electrons, can gain one electron to provide it with 36 electrons. A discussion of the theory supporting the favored status of noble gas electron numbers reflected in these predictive rules for ion formation is provided in a later chapter of this text.
Compound containing both ionic and covalent bonds
If you know the chemical formula of a compound, you can predict whether it contains ionic bonds, covalent bonds, or a mixture of bond types. Nonmetals bond to each other via covalent bonds while oppositely charged ions, such as metals and nonmetals, form ionic bonds. Compounds which contain polyatomic ions may have both ionic and covalent bonds. But, how do you know if a compound is ionic or covalent just by looking at a sample? This is where the properties of ionic and covalent compounds can be useful.
Ladyboy hot video
Suggested Exams. FCI Manager. BRO Operator Communication. JEE Main. Rajasthan High Court Civil Judge. Maharashtra Nagar Parishad Fire Officer. ACC Exam. Maharashtra Zilla Parishad Supervisor. Learn today! JNU Junior Assistant. Rajasthan PTET. Create profiles for personalised advertising.
What elements make covalent bonds?
Gujarat Metro Maintainer. Punjab Police SI. Shared pair or bonding pair refers to the pair of electrons involved in this sort of bonding. Cochin Shipyard Executive Trainee. AAI Junior Assistant. Delhi Police MTS. Karnataka Forest Guard. The complete transfer of one or more electrons from one atom to the other forms a chemical link between two atoms, causing the atoms to acquire their closest inert gas configuration. India Post. India Post Mail Guard. Gujarat TAT. Maharashtra Zilla Parishad Health Supervisor. Bihar STET. CTU Conductor. Karnataka TET.

I join. And I have faced it. Let's discuss this question.
In my opinion you are mistaken. I suggest it to discuss.
I know nothing about it