Chorda tympani
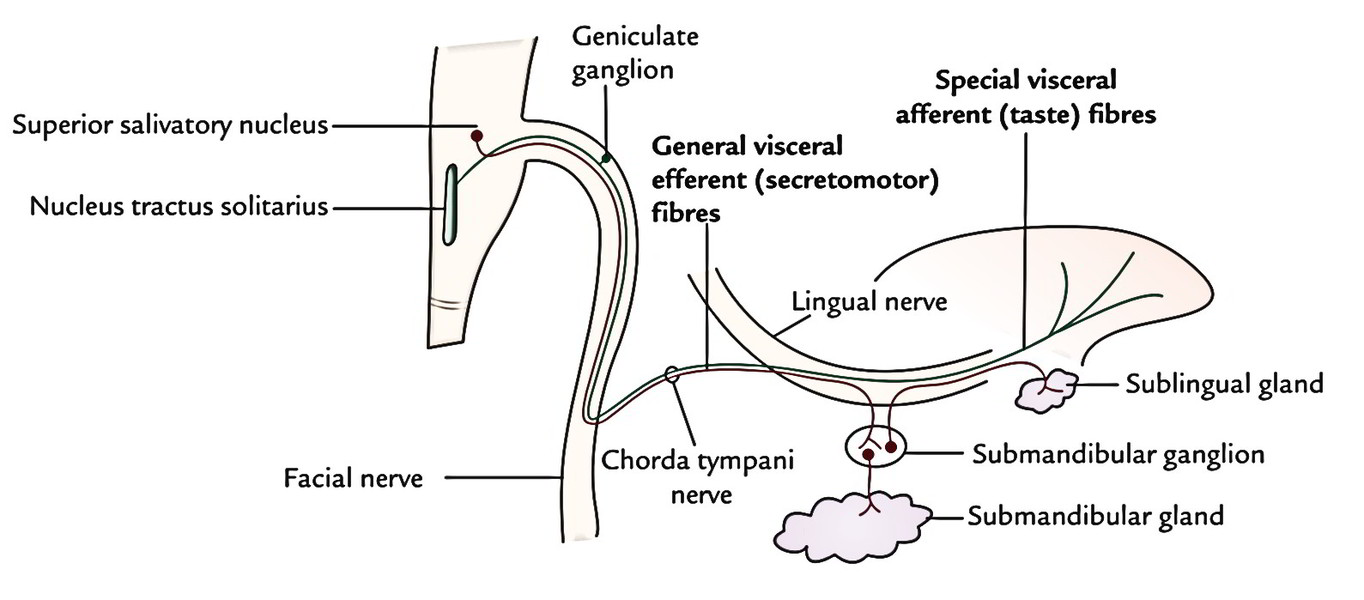
The Chorda Tympani Nerve is given off from the facial as it passes downward behind the tympanic cavity, about 6 mm, chorda tympani. It then descends between the Pterygoideus externus and internus on the medial surface of the spina angularis of the sphenoid, which it sometimes grooves, chorda tympani, and joins, at an acute angle, the posterior border of the lingual nerve. It receives a few efferent fibers from the motor root; these enter the submaxillary ganglion, and through chorda tympani are distributed to the submaxillary and sublingual glands; the majority of its fibers are afferent, and are continued onward through the muscular substance of the tongue to the mucous membrane covering its anterior two-thirds; they constitute the nerve of taste for this portion of the tongue.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Ashnaa Rao ; Prasanna Tadi.
Chorda tympani
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made. The chorda tympani is a nerve that arises from the mastoid segment of the facial nerve , carrying afferent special sensation from the anterior two-thirds of the tongue via the lingual nerve , as well as efferent parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual glands. After branching off from the facial nerve, the chorda tympani courses through the temporal bone before joining the lingual nerve 2 :. The distance of ascent is variable, depending on the initial branching pattern from the mastoid segment of facial nerve. It then travels inferiorly to join the lingual nerve approximately 2 cm below the skull base. Articles: Middle ear tumours Lingual nerve Anterior tympanic artery Retrotympanum Tongue Parasympathetic nervous system Nervus intermedius Middle ear Mesotympanum Petrotympanic fissure Infratemporal fossa Greater wing of sphenoid Sublingual gland Tympanic membrane Facial nerve Submandibular ganglion Submandibular gland Cases: Anatomy of the genicular ganglion Gray's illustration Trigeminal and facial nerve connections illustration Facial nerve anatomy - labeled CT Chorda tympani Multiple choice questions: Question Please Note: You can also scroll through stacks with your mouse wheel or the keyboard arrow keys. Updating… Please wait. Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again. Thank you for updating your details.
Middle ear damages. Table of Contents.
Chorda tympani is a branch of the facial nerve that carries gustatory taste sensory innervation from the front of the tongue and parasympathetic secretomotor innervation to the submandibular and sublingual salivary glands. Chorda tympani has a complex course from the brainstem , through the temporal bone and middle ear , into the infratemporal fossa , and ending in the oral cavity. Chorda tympani fibers emerge from the pons of the brainstem as part of the intermediate nerve of the facial nerve. The facial nerve exits the cranial cavity through the internal acoustic meatus and enters the facial canal. Within the facial canal, chorda tympani branches off the facial nerve and enters the lateral wall of the tympanic cavity within the middle ear , where it runs across the tympanic membrane from posterior to anterior and medial to the neck of the malleus. Chorda tympani then exits the skull by descending through the petrotympanic fissure into the infratemporal fossa.
The Chorda Tympani Nerve is given off from the facial as it passes downward behind the tympanic cavity, about 6 mm. It then descends between the Pterygoideus externus and internus on the medial surface of the spina angularis of the sphenoid, which it sometimes grooves, and joins, at an acute angle, the posterior border of the lingual nerve. It receives a few efferent fibers from the motor root; these enter the submaxillary ganglion, and through it are distributed to the submaxillary and sublingual glands; the majority of its fibers are afferent, and are continued onward through the muscular substance of the tongue to the mucous membrane covering its anterior two-thirds; they constitute the nerve of taste for this portion of the tongue. Before uniting with the lingual nerve the chorda tympani is joined by a small branch from the otic ganglion. Human anatomy 2. Underlying structures:. Human anatomy 1. Underlying structures: There are no anatomical children for this anatomical part.
Chorda tympani
In this article, we shall look at the anatomy of the facial nerve — its anatomical course, functions and clinical correlations. The facial nerve is associated with the derivatives of the second pharyngeal arch :. The course of the facial nerve is very complex. There are many branches, which transmit a combination of sensory, motor and parasympathetic fibres. The nerve arises in the pons , an area of the brainstem. It begins as two roots; a large motor root , and a small sensory root the part of the facial nerve that arises from the sensory root is sometimes known as the intermediate nerve. The two roots travel through the internal acoustic meatus, a 1cm long opening in the petrous part of the temporal bone. Here, they are in very close proximity to the inner ear. Still within the temporal bone, the roots leave the internal acoustic meatus, and enter into the facial canal. Within the facial canal, three important events occur:.
Bigcutie lily
Help Accessibility Careers. Figure Chorda tympani Image courtesy O. Tympanic tympanic plexus lesser petrosal otic ganglion Stylopharyngeal branch Pharyngeal branches Tonsillar branches Lingual branches Carotid sinus. These cookies are used to measure audience: it allows to generate usage statistics useful for the improvement of the website. Additionally, it carries parasympathetic general visceral efferent fibers to the submandibular ganglion that innervate the sublingual and submandibular glands. It then descends close to the spine of the sphenoid bone and merges with a branch of the mandibular nerve, the lingual nerve. Taste damage, especially, can be long-lasting, most notably if it involves bitterness. In addition, it causes the blood vessels in the tongue to dilate open wider , which is called vasomotor function. This has been proven by anesthetizing the chorda tympani, which increases pain sensation and the perception of certain flavors, especially salt. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page.
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
The facial nerve consists of two parts:. A decreased taste sensitivity or distortions in taste perception can result from drug use and a variety of medications and is even associated with viral infections, psychiatric disorders, and Bell Palsy. Clinical Significance A vestibular schwannoma or acoustic neuroma may result in the loss of function of the chorda tympani on the ipsilateral side; this is often also associated with paralysis of ipsilateral facial muscles and impaired secretions of the lacrimal, submandibular, and sublingual glands. After branching off from the facial nerve, the chorda tympani courses through the temporal bone before joining the lingual nerve 2 :. Experts theorize that this kind of inhibition may help the brain accurately classify a broader range of tastes and other sensations. Essential technical cookies These are cookies that ensure the proper functioning of the website and allow its optimization detect browsing problems, connect to your IMAIOS account, online payments, debugging and website security. Chemical Senses. Finally, the stylomastoid branch of the posterior auricular artery has two branches that supply the remaining portions of the facial nerve. Share Feedback. Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy [ edit on Wikidata ]. Cookie preferences Continue without accepting. It also sends a branch to the parotid gland in the cheek.

0 thoughts on “Chorda tympani”