Cholinesterase
The enzyme cholinesterase EC 3.
Cholinesterase is an enzyme that helps your nervous system work the way it should. Certain toxic chemicals in the environment can interfere with this enzyme and affect your nervous system. These chemicals include organophosphates and carbamates. They are most often found in insecticides used in fields. They have also been used as chemical warfare agents. These chemicals can be found in common household insect sprays, too.
Cholinesterase
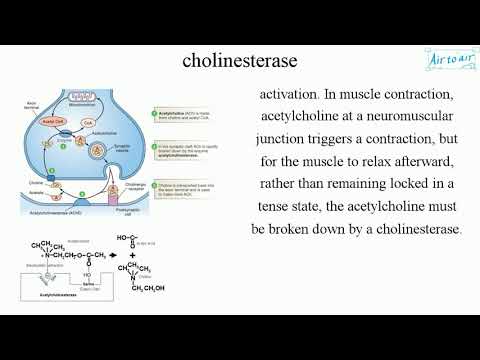
Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors which, for brevity, we will refer to as cholinesterase inhibitors are chemicals whose primary toxic effect is to block the normal breakdown of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine. This normal breakdown is shown in Figure 1 below. They do this by occupying and blocking the site where the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine , attaches to the enzyme, acetylcholinesterase. If you are interested in the details at the chemical level, see the Optional Reading below. Figure 2 below shows how a cholinesterase inhibitor in this case, a nerve agent attaches to the serine hydroxyl group on acetylcholinesterase. This prevents acetylcholine from interacting with the cholinesterase enzyme and being broken down. Diagrams modified from Wiener, S. Figure 2. Partially electropositive phosphorus is attracted to partially electronegative serine. Figure 4. Cholinesterase inhibitor attached to acetylcholinesterase preventing the attachment of acetylcholine. This leads to the build up of excessive levels of the neurotransmitter, acetylcholine , at the skeletal neuromuscular junction and those synapses where acetylcholine receptors are located. Thus, the primary manifestations of acute cholinesterase inhibitor toxicity are those of cholinergic neurotransmitter hyperactivity. Carlton, Simpson et al.
Blood can be drawn to cholinesterase RBC cholinesterase activity if there is difficulty confirming the diagnosis. The cholinesterase inhibitor drugs inhibit AChE activity and maintain the ACh level by decreasing its breakdown rate, cholinesterase.
Cholinesterase inhibitors ChEIs , also known as anti- cholinesterase , are chemicals that prevent the breakdown of the neurotransmitter acetylcholine or butyrylcholine. This increases the amount of the acetylcholine or butyrylcholine in the synaptic cleft that can bind to muscarinic receptors , nicotinic receptors and others. ChEIs may be used as drugs for Alzheimer's and myasthenia gravis , and also as chemical weapons and insecticides. ChEIs are indirect-acting parasympathomimetic drugs. ChEls are widely used as chemical weapons.
Serum cholinesterase is a blood test that looks at levels of 2 substances that help the nervous system work properly. They are called acetylcholinesterase and pseudocholinesterase. Your nerves need these substances to send signals. Acetylcholinesterase is found in nerve tissue and red blood cells. Pseudocholinesterase is found primarily in the liver. Acetylcholinesterase; RBC or erythrocyte cholinesterase; Pseudocholinesterase; Plasma cholinesterase; Butyrylcholinesterase; Serum cholinesterase. A blood sample is needed.
Cholinesterase
A series of quinazolin-4 3H -one derivatives was designed through scaffold-hopping strategy and synthesized as novel multifunctional anti-AD agents demonstrating both cholinesterase inhibition and anti-inflammatory activities. Their inhibitory activities against acetylcholinesterase AChE and butyrylcholinesterase BChE were evaluated, and the enzyme kinetics study as well as detailed binding mode via molecular docking were performed for selected compounds. All these results indicate that MR is a good starting point to develop multifunctional anti-AD lead compounds. Keywords: Acetylcholinesterase; Alzheimer's disease; Butyrylcholinesterase; Multifunctional inhibitor; Quinazolin-4 3H -one; anti-inflammatory activity. Abstract A series of quinazolin-4 3H -one derivatives was designed through scaffold-hopping strategy and synthesized as novel multifunctional anti-AD agents demonstrating both cholinesterase inhibition and anti-inflammatory activities. Substances Cholinesterase Inhibitors Butyrylcholinesterase Acetylcholinesterase.
Photoshoot peg
Indications Cholinesterase inhibitors also have the following names: acetylcholinesterase AChE inhibitors or anticholinesterases. The Eye. Different forms can be available for different types of cholinesterase inhibitors. Afterward, the site may be sore. Due to the ability to increase vagal tone through activation of the parasympathetic nervous system, caution is necessary when administering cholinesterase inhibitors to individuals who have bradycardia or cardiac conduction diseases such as sick sinus syndrome. Information developed by A. Describe how cholinesterase inhibitors, including organophosphorus compounds e. J Neurol Sci. Curr Neuropharmacol. It triggers the stimulation of post-synaptic nerves, muscles, and exocrine glands. FDA access data. Further information: Organophosphate poisoning and cholinergic crisis. Reevaluation and update on efficacy and safety of neostigmine for reversal of neuromuscular blockade.
Official websites use. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Call for all medical emergencies. If these chemicals get into your body, they can affect how you breathe and can cause general muscle weakness. Cholinesterase inhibitors are also necessary to administer when anticholinergic poisoning is suspected. Drug class. They SEe use in the treatment of Alzheimer and dementia symptoms. Retrieved 24 August How you are exposed, such as by breathing, eating or drinking, or skin contact. You don't need to prepare for this test. Archived PDF from the original on These include bleeding, infection, bruising, and feeling lightheaded.

0 thoughts on “Cholinesterase”