Cassava macros
Cassava is a root vegetable that contains vitamin C and copper, cassava macros. It may also contain harmful compounds if consumed raw.
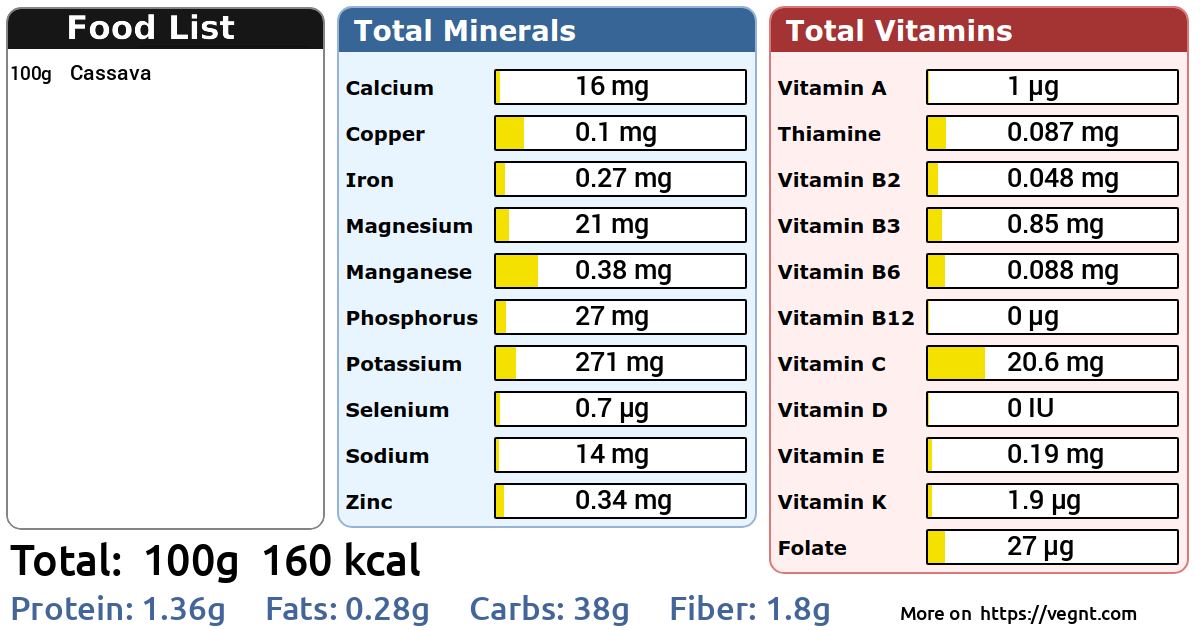
Cassava is a nutrient-dense, starchy root vegetable consumed in developing countries around the world. It's also known as yucca , manioc, or mandioca. Because cassava produces a natural toxin, some people are wary of eating it. However, the right preparation methods prevent this from being an issue. When cooked, cassava has a similar texture to potatoes. Its tuberous roots are used to make cassava flours, breads, and tapioca. The nutrition information is provided by the USDA for 1 cup grams of raw cassava.
Cassava macros
Register Sign In. Search in:. My FatSecret. Food database and calorie counter. Last updated: 04 Feb 08 AM. Calorie Breakdown:. Nutrition summary: Calories. Food Search. Save Refresh Cancel. Please note that some foods may not be suitable for some people and you are urged to seek the advice of a physician before beginning any weight loss effort or diet regimen. Although the information provided on this site is presented in good faith and believed to be correct, FatSecret makes no representations or warranties as to its completeness or accuracy and all information, including nutritional values, is used by you at your own risk. All trademarks, copyright and other forms of intellectual property are property of their respective owners. Get the app. All rights reserved. United States.
Calorie Breakdown:. This article determines….
.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Besides the wide use of its roots, cassava leaves have been used locally as green vegetables and for medicinal purposes. However, nutritional health data regarding cassava leaves is limited, therefore we investigated its composition and associated potential bioactivity interest for human health. The plant world is a major source of compounds with nutrition and health potential. Natural bioactive products are recognized for their beneficial effects in various human diseases. They are of great interest to researchers due to their broad structural diversity and wide range of biological activities [ 1 ]. Among them, cassava Manihot esculenta Crantz is known for its floury, starchy root, and is widely consumed in tropical regions of Africa, Asia and Latin America. Therefore, cassava is mainly grown as a root crop for human consumption as a source of carbohydrates. Nonetheless, in some regions, cassava leaves are consumed as green vegetables and are used in traditional medicines.
Cassava macros
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Diversity in the mineral composition of cassava leaves bred in sub-Saharan Africa has not been fully investigated. This study characterized macro and micro-minerals in genotypes of Cassava leaves planted in three different agroecological environments in Nigeria. Laboratory analysis of the leaves was done using an Inductively Coupled Optical Emission Spectrometer. When the location effect was tested, there was a significant difference among the genotypes for all elements. Cluster analysis resulted in five clusters containing , , 60, 2, and 4 genotypes, respectively.
Muchova wikipedia
The most commonly consumed part of the cassava plant is the root, which is incredibly versatile. Overall, cassava is a great source of carbohydrates, and provides high amounts of vitamin C and potassium. Cassava is high in resistant starch , a type of starch that bypasses digestion and has properties similar to those of soluble fiber. Cassava, raw. Still, cooking the root before consumption is necessary to avoid side effects Variants have also been introduced that are higher in vitamin A and beta carotene to better support the nutritional needs of those who rely on it as a staple crop. Vitamin C also protects against skin damage and stimulates the production of collagen, a type of protein found throughout your body in your bones, skin, muscles, and joints Share Feedback. Register Sign In. Ethnopharmacological values of cassava and its potential for diabetes and dyslipidemia management: Knowledge survey and critical review of report. Use profiles to select personalised content. Regularly consuming cyanogenic glycosides or eating them in high amounts increases the risk of cyanide poisoning. Try this today: You can easily swap other root vegetables for cassava in your favorite recipes to add some diversity to your diet.
What is cassava flour? You also might have hard of another popular product made from cassava: tapioca. Tapioca is usually found in stores in the form of small, white pearls made from extracted cassava starch.
From carrots to potatoes to onions, root vegetables have long been enjoyed as a delicious part of a healthy diet — and for good reason. Nutrition Facts. Note that products made from the root, such as cassava flour and tapioca, contain little to no cyanide-inducing compounds and are safe to eat. Aside from being a nutritious vegetable that can contribute to a balanced diet, there are some other benefits to eating cassava. Starch Health Benefits Researchers say resistant starches can help with weight loss, and perhaps even reduce risks associated with diabetes and colon cancer. It's also known as yucca , manioc, or mandioca. The bottom line. La Choy Bean Sprouts g. Bibigo Vegetable Fried Rice. You're likely to find cassava at any time of the year, if not in your local supermarket, then in an Asian, South American, or African grocer. University of California Cooperative Extension. While eating raw potatoes may be linked to several benefits, there are also some safety and nutrition concerns to consider. Happy Harvest Crushed Tomatoes 61g. There are just under 2 grams of both fiber and natural sugars in a serving of cassava.

0 thoughts on “Cassava macros”