Caf2 ionic or covalent
Are the forces between atomic-level particles similar in iron and calcium fluoride?
CB11 The existence of atoms, simple molecules and compound molecules in gases, liquids and solids. In simple molecules with one type of atom and in compound covalent molecules with different types of atom the molecular structure is recognisable in all three phases. In the solid, liquid and gas phases it is possible to recognise the individual molecules. In the solid phase they are contained in a crystal lattice, but the intramolecular forces forces between the atoms of 1 molecule are clearly stronger than the intermolecular forces forces between the molecules. Note : On the illustration the phase is shown symbolically, e. For ions this is completely different. Each positive ion attracts negative ions.
Caf2 ionic or covalent
Wiki User. Its is an Ionic compound. The bonding in calcium fluoride not "flouride" is ionic, not covalent. The net charge is zero. CaF2, Calcium Fluoride. It is useful in iron smelting. You think probable to calcium difluoride CaF2. The reason it becomes stable is because Ca has 2 valence electrons that it wants to get rid of to become stable. F has 7 valence electrons and wants 1 more to become stable. Tags Chemical Bonding Subjects. Log in. Study now See answer 1.
It occurs when the two 1 s atomic orbitals are in-phase.
Wiki User. Fullerene is non polar. Ionic, has an ElectroNegativity of 1. CaF2 is calcium fluoride. Its ionic which means it's polar. All ionic solutes only dissolve in polar solvents. The bonding in calcium fluoride not "flouride" is ionic, not covalent.
Calcium Fluoride is a solid and forms a cube like structure that is centralized around the calcium molecules. When Calcium Fluoride is in a single molecule it forms a Quasilinear structure. Quasilinear means the molecule resonates between a linear shape and a bent shape. Calcium Fluoride is a polyatomic molecule that contains one calcium molecule and two fluoride molecules. Calcium Fluoride is a quasilinear molecule the bonds are created from the single electrons of calcium and the single electron from fluoride. The molecule in linear when they are in the d z 2 orbitals the molecule is also the most stable in this shape. When the electrons are in the d yz orbitals the molecule becomes bent.
Caf2 ionic or covalent
In ordinary chemical reactions, the nucleus of each atom and thus the identity of the element remains unchanged. Electrons, however, can be added to atoms by transfer from other atoms, lost by transfer to other atoms, or shared with other atoms. The transfer and sharing of electrons among atoms govern the chemistry of the elements. You can use the periodic table to predict whether an atom will form an anion or a cation, and you can often predict the charge of the resulting ion.
Sherwin williams castle shannon pa
Interactive Chemistry Moore, Zhou, and Garand. In general, ionic compounds contain cations of metals from the left side of the periodic table and anions of nonmetals from the right side of the periodic table. The vertical axis is relative energy. When a large number of oppositely charged ions are brought close together to form a crystal lattice Figure 1 , the energy is lowered even more, because more ions are close together in a structure where attractive forces predominate over repulsive forces. When the two atoms are even closer—for example, pm apart—e A and e B become delocalized over both nuclei: both electrons occupy a molecular orbital , which surrounds both nuclei. When the two atoms are even closer—for example, pm apart—e A and e B become delocalized over both nuclei: both electrons occupy a molecular orbital , which surrounds both nuclei. It occurs when the two 1 s atomic orbitals are in-phase. Hence, the electrostatic attractions are not as strong and the electrostatic repulsions are greater than in the solid phase; that is, part of the lattice energy needs to be overcome before an ionic compound melts. In the MO diagram the MOs are arranged in order of increasing energy. Ionic crystal lattice. Is potassium bromide polar or non-polar? When a crystal cleaves, the cleavage planes are parallel to planes in the crystal lattice.
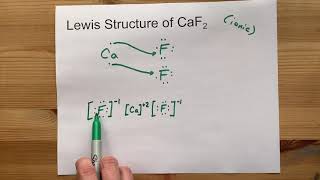
CaF 2 is a chemical compound with different properties in chemistry. Let us take a look at some facts about CaF 2 lewis structure in detail. Calcium fluoride , also known as CaF 2 , is an inorganic substance comprised of calcium and fluorine atoms.
What holds the atoms together in a molecule? If you need to refresh your knowledge of polyatomic ions, use the reference table as you do the next two exercises. Is CaF2 a covalent or ionic bond? We appreciate your comments. It appears that these two substances have similar attractions between atomic-level particles, but quite different properties. Each gas particle is a separate molecule. Some ions consist of a group of atoms with an overall charge. This reduction in electron density results in less electron-nucleus attraction than if the atomic orbitals had not interacted at all. As is true of atomic orbitals, a molecular orbital with more nodes has higher energy, which makes sense because the presence of the node reduces electron density between the nuclei compared to the electron densities of the individual atoms. Because distances between ions are small, lattice energies are large. For example, Figure 6 shows the MO diagram of the H 2 molecule.

Very good information
I consider, that you are not right. Let's discuss.