Boron trifluoride shape
The molecular formula of boron trifluoride BF 3 indicates that it has one boron B atom and three fluorine F atoms. Boron is located in Group 13 of the periodic boron trifluoride shape. It has three valence electrons. Fluorine is located in Group 17 and has seven valence electrons.
Total: 0. Colourless, heavier-than-air gas with a pungent odour. It forms white fumes in moist air. Boron trifluoride is a colourless , toxic gas with a pungent smell and greater density than air. It forms white smoke during hydrolysis caused by exposure to humid air. It dissolves well in water while forming hydrogen and boric acid. It reacts intensely with metals.
Boron trifluoride shape
The valence bond theory also predicts a planar triangle with hybridisation of one s and two p orbitals used for bonding. However, the B atom only has six electrons in its outer shell and this is termed electron deficient. The empty 2p z atomic orbital on B which is not involved in hybridisation is perpendicular to the triangle containing the sp 2 hybrid orbitals. This p z orbital may accept an electron pair from a full p z orbital on any one of the three fluorine atoms. If one localized double bond existed, then there would be one short bond and two longer ones. However, all measurements show that the three bond lengths are identical. The old valence bond explanation of this was resonance between three structures with the double bond in different positions. The modern explanation is that the double bond is delocalised. The order is the reverse of what would be normally expected on the basis of electronegativity of halogen and also on the basis of steric grounds. Home What is the boron trifluoride formula?
As SF boron trifluoride shape is octahedral, there are six degree bond angles between sulphur and fluorine, degree angles between each fluorine and its four closest neighbours and a degree angle between each fluorine and its opposite fluorine. Get subscription.
In this article, you will read about BF3 molecular geometry. The inorganic compound is boron trifluoride with formula BF 3. BF 3 is colourless, poisonous gas that has no colour. In damp air, it releases white vapours and is soluble if it is in the form of a colourless liquid i. This plane seems like all peripheral atoms exist in one place. For determining the lewis structure, you need to calculate the total number of valence electrons for the BF 3 molecule.
You may have heard about the chemical compound that lacks C-H bonds. Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound, and its formula is BF3. It does not contain any color, and it is a toxic gas. It creates white fumes in the moist air. If it is in the form of a colorless liquid, it is very soluble dihydrate.
Boron trifluoride shape
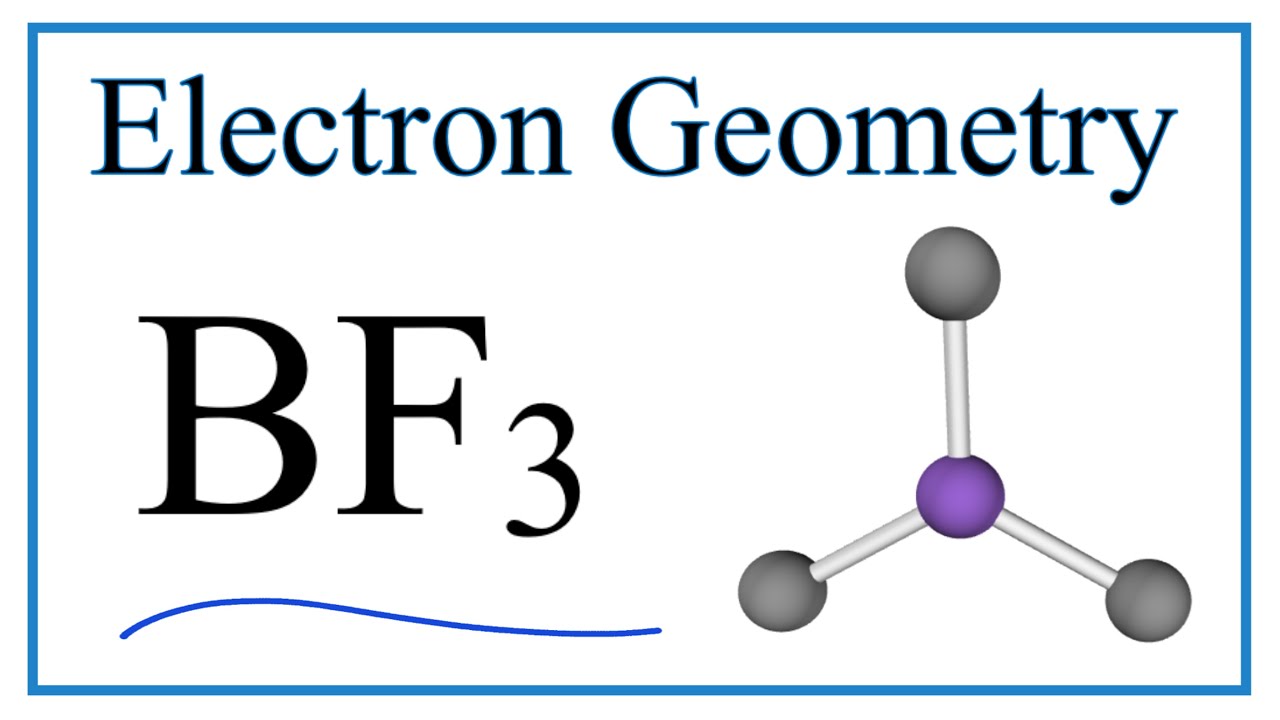
Boron trifluoride is the inorganic compound with the formula BF 3. This pungent, colourless, and toxic gas forms white fumes in moist air. It is a useful Lewis acid and a versatile building block for other boron compounds. The geometry of a molecule of BF 3 is trigonal planar. The molecule has no dipole moment by virtue of its high symmetry. BF 3 is commonly referred to as " electron deficient ," a description that is reinforced by its exothermic reactivity toward Lewis bases. In the boron trihalides, BX 3 , the length of the B—X bonds 1. A facile explanation invokes the symmetry-allowed overlap of a p orbital on the boron atom with the in-phase combination of the three similarly oriented p orbitals on fluorine atoms. BF 3 is manufactured by the reaction of boron oxides with hydrogen fluoride :. Typically the HF is produced in situ from sulfuric acid and fluorite CaF 2.
Personalised jigsaw puzzles 1000 pieces
References Whatsinsight. Define back bonding in BF3. I would like to stay signed in. How Haloform reaction proceed? However, the B atom only has six electrons in its outer shell and this is termed electron deficient. Access free live classes and tests on the app. Exception 2 : If the octet has very few valence electrons Exception 3 : If the strict has too many valence electrons. Types of Impurity Defects. The empty 2p z atomic orbital on B which is not involved in hybridisation is perpendicular to the triangle containing the sp 2 hybrid orbitals. The central atom can be BF 3 which has 24 valence electrons, which must be rearranged around it. BF3 Hybridization Hybridization is the process of combining atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. Boron will be the least electronegative element at the core of its structure, and its outer shell also needs six valence electrons. Zeolites have small, fixed-size openings that allow small molecules to pass through easily but not larger molecules; this is why they are sometimes referred to as molecular sieves.
The molecular formula of boron trifluoride BF 3 indicates that it has one boron B atom and three fluorine F atoms. Boron is located in Group 13 of the periodic table. It has three valence electrons.
Types of Impurity Defects. Each fluorine atom will have six lone pairs []. In this article, you will read about BF3 molecular geometry. Boron has three valence atomic orbitals forming three sp2 hybridized orbitals — one 2s and two 2p orbitals. Van der Waals Equation. What is the NH3 bond angle? As a result, you can say the BF 3 molecule is nonpolar. Exception 2 : If the octet has very few valence electrons Exception 3 : If the strict has too many valence electrons. Quantity: 0. Types of Chemical Reactions. Get subscription. BF3 Hybridization Hybridization is the process of combining atomic orbitals to form new hybrid orbitals. So, it will lie at the center of the molecule. Due to sp 2 -hybridization, BF 3 and AlF 3 have a trigonal symmetric structure. The inorganic compound is boron trifluoride with formula BF 3.

0 thoughts on “Boron trifluoride shape”