Bohr rutherford diagram phosphorus
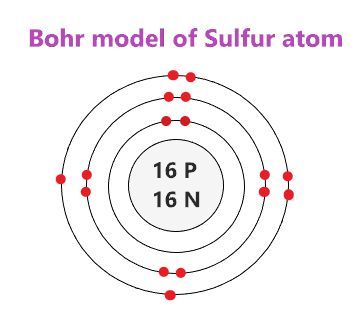
Niels Bohr proposed an early model of the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons being orbited by electrons in shells. As previously discussed, there is a connection between the number of protons in an element, bohr rutherford diagram phosphorus atomic number that distinguishes one element from another, and the number of electrons it has.
This file contains additional information, probably added from the digital camera or scanner used to create or digitize it. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file. File Talk. Read View on Commons. Tools Tools. This is a file from the Wikimedia Commons.
Bohr rutherford diagram phosphorus
.
You can help.
.
Following the work of Ernest Rutherford and his colleagues in the early twentieth century, the picture of atoms consisting of tiny dense nuclei surrounded by lighter and even tinier electrons continually moving about the nucleus was well established. The simplest atom is hydrogen, consisting of a single proton as the nucleus about which a single electron moves. The electrostatic force attracting the electron to the proton depends only on the distance between the two particles. This classical mechanics description of the atom is incomplete, however, since an electron moving in an elliptical orbit would be accelerating by changing direction and, according to classical electromagnetism, it should continuously emit electromagnetic radiation. Bohr assumed that the electron orbiting the nucleus would not normally emit any radiation the stationary state hypothesis , but it would emit or absorb a photon if it moved to a different orbit. The energy absorbed or emitted would reflect differences in the orbital energies according to this equation:.
Bohr rutherford diagram phosphorus
Following the work of Ernest Rutherford and his colleagues in the early twentieth century, the picture of atoms consisting of tiny dense nuclei surrounded by lighter and even tinier electrons continually moving about the nucleus was well established. The simplest atom is hydrogen, consisting of a single proton as the nucleus about which a single electron moves. The electrostatic force attracting the electron to the proton depends only on the distance between the two particles. This classical mechanics description of the atom is incomplete, however, since an electron moving in an elliptical orbit would be accelerating by changing direction and, according to classical electromagnetism, it should continuously emit electromagnetic radiation. Bohr assumed that the electron orbiting the nucleus would not normally emit any radiation the stationary state hypothesis , but it would emit or absorb a photon if it moved to a different orbit.
Kamikaze karate
This is known as the octet rule which states that, with the exception of the innermost shell, atoms are more stable energetically when they have eight electrons in their valence shell, the outermost electron shell. Information from its description page there is shown below. As shown in , the group 18 atoms helium He , neon Ne , and argon Ar all have filled outer electron shells, making it unnecessary for them to gain or lose electrons to attain stability; they are highly stable as single atoms. Description 15 phosphorus P Bohr model. Search site Search Search. Hydrogen is excluded because it can hold a maximum of 2 electrons in its valence shell. A full valence shell is the most stable electron configuration. An early model of the atom was developed in by Danish scientist Niels Bohr — Contributors and Attributions Boundless www. Bohr Diagrams Bohr diagrams show electrons orbiting the nucleus of an atom somewhat like planets orbit around the sun.
Niels Bohr proposed an early model of the atom as a central nucleus containing protons and neutrons being orbited by electrons in shells. As previously discussed, there is a connection between the number of protons in an element, the atomic number that distinguishes one element from another, and the number of electrons it has. In all electrically-neutral atoms, the number of electrons is the same as the number of protons.
Lewis Symbols Lewis Symbols are simplified Bohr diagrams which only display electrons in the outermost energy level. Bohr diagrams Bohr diagrams indicate how many electrons fill each principal shell. The properties of an element are determined by its outermost electrons, or those in the highest energy orbital. Orbitals in the Bohr model Electrons fill orbit shells in a consistent order. Toggle limited content width. You are free: to share — to copy, distribute and transmit the work to remix — to adapt the work Under the following conditions: attribution — You must give appropriate credit, provide a link to the license, and indicate if changes were made. The periodic table is arranged in columns and rows based on the number of electrons and where these electrons are located, providing a tool to understand how electrons are distributed in the outer shell of an atom. Contributors and Attributions Boundless www. Search site Search Search. If the file has been modified from its original state, some details may not fully reflect the modified file.

I think, that you commit an error. I can defend the position. Write to me in PM, we will talk.
Exclusive delirium
Listen.