Bbc bitesize plant cell
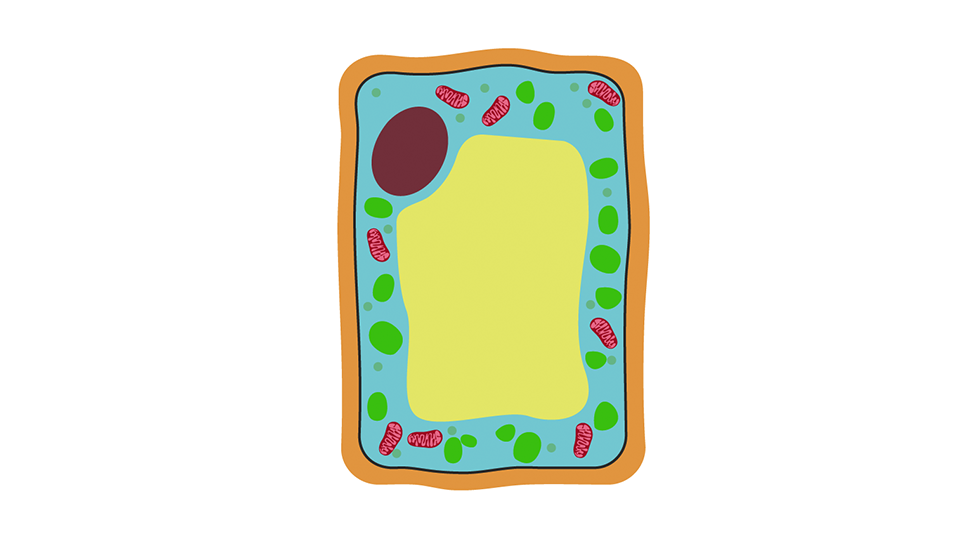
Most life on Earth depends upon plants for energy. Plants capture light from the sun and use it to build up chemical stores of energy. This is called photosynthesis. The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below.
The basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. There are many different types of cells in plants. Each type is specialised to do a particular role and ensures that the organism functions as a whole. There are no top and bottom walls between xylem vessels, so there is a continuous column of water running through them.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below - the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with a transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. In this guide. Cell measurement Electron microscopes Animal cells Plant cells Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Investigating cells with a light microscope Measuring cell size Comparing sizes. Plant cells. Animal and plant cells have certain structures in common. Cell structure How it is related to its function Cytoplasm A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles. It is where many of the chemical reactions happen. Nucleus Contains genetic material, including DNA, which controls the cell's activities. Cell membrane Its structure is permeable to some substances but not to others, it therefore controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Mitochondria Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration. Ribosomes A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs. Cell structure Cytoplasm How it is related to its function A jelly-like material that contains dissolved nutrients and salts and structures called organelles.
Biology: Exam-style questions Bitesize revision podcasts Personalise your Bitesize! Phloem cells are often found near to xylem cells in the stem. The nucleus contains DNA deoxyribonucleicacid.
This basic structure of a plant cell is shown below — the same plant cell, as viewed with the light microscope, and with the transmission electron microscope. Animal cells may also have vacuoles, but these are small and temporary. In animals, they are commonly used to store or transport substances. In this guide. Cell measurement Cell size Preparing biological samples for examination Investigating cells with a light microscope Microscopes The limits of the light microscope Animal cells Plant cells Measuring cell size Comparing sizes Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Plant and animal cells. Plant cells.
Inside cells are various structures that are specialised to carry out a particular function. Both animal and plant cells have these components:. Red blood cells are some of the smallest cells in the human body. These have a diameter of 0. The ovum or egg cell is one of the largest cells in the human body. It has a diameter of roughly 0.
Bbc bitesize plant cell
Models in science are used to help us understand complicated ideas in a simple and memorable way. Place the neck of the balloon over a tap and fill it with water. There you go! You've now made your very own model of an animal cell. Cell membrane close cell membrane This surrounds the outside of animal cells and controls what can enter and exit it. Cytoplasm close cytoplasm The liquid that makes up most of the cell in which chemical reactions happen.
Penpods
Cell measurement Cell size Preparing biological samples for examination Investigating cells with a light microscope Microscopes The limits of the light microscope Animal cells Plant cells Measuring cell size Comparing sizes Eukaryotes and prokaryotes Plant and animal cells. In this guide. Organelles that contains the green pigment, chlorophyll, which absorbs light energy for photosynthesis. This video can not be played To play this video you need to enable JavaScript in your browser. Plant cells. More guides on this topic. I've always been fascinated with bodies, with animals, with humans, how they work, what they're made up of. Cell wall Function Made from cellulose fibres and strengthens the cell and supports the plant. Cells are the smallest unit of life and the building blocks for all organisms. Plant cells. Cell structure Mitochondria How it is related to its function Organelles that contain the enzymes for respiration, and where most energy is released in respiration. It therefore controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
Many cells in multicellular organisms are specialised. They have specific roles in the organism of which they are part. Their structure is adapted to their function.
Related links. Ribosomes Tiny organelles where protein synthesis occurs. Water will diffuse from a higher water concentration inside the cell to a lower water concentration outside the cell. Animal cells often have an irregular shape. Location of reactions in anaerobic respiration. Cell structure Ribosomes How it is related to its function A tiny organelle where protein synthesis occurs. Tilly: The best thing about being a butcher, I would say for me is talking about how to cook meat, how it's raised, and seeing people choose to buy ethical and sustainable meat. Here respiration close respiration A chemical reaction that occurs in the mitochondria of cells in which glucose and oxygen react to produce carbon dioxide and water, releasing energy. Biology: Exam-style questions Bitesize revision podcasts Personalise your Bitesize! Find out how to spot risks, hazards and understand hazard symbols. Cell wall Plant and bacterial cell walls provide structure and protection.

Consider not very well?