Baroreceptors
Klabunde Arterial blood pressure is normally regulated within a narrow range, with a mean arterial pressure baroreceptors ranging from 85 to mmHg in adults. It is important to control arterial pressure to ensure baroreceptors blood flow to organs throughout the body. This is accomplished by negative feedback systems incorporating pressure sensors i, baroreceptors.
Federal government websites often end in. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site. The site is secure. NCBI Bookshelf. Yasaman Pirahanchi ; Bruno Bordoni.
Baroreceptors
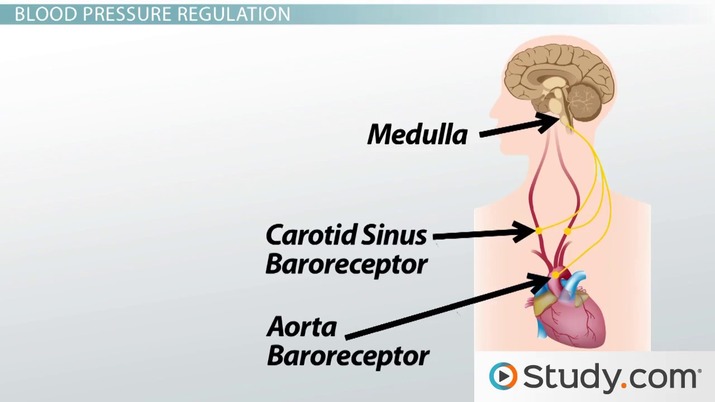
The baroreflex or baroreceptor reflex is one of the body's homeostatic mechanisms that helps to maintain blood pressure at nearly constant levels. The baroreflex provides a rapid negative feedback loop in which an elevated blood pressure causes the heart rate to decrease. Decreased blood pressure decreases baroreflex activation and causes heart rate to increase and to restore blood pressure levels. Their function is to sense pressure changes by responding to change in the tension of the arterial wall [1] The baroreflex can begin to act in less than the duration of a cardiac cycle fractions of a second and thus baroreflex adjustments are key factors in dealing with postural hypotension , the tendency for blood pressure to decrease on standing due to gravity. The system relies on specialized neurons , known as baroreceptors , chiefly in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses , to monitor changes in blood pressure and relay them to the medulla oblongata. Baroreceptors are stretch receptors and respond to the pressure induced stretching of the blood vessel in which they are found. Baroreflex-induced changes in blood pressure are mediated by both branches of the autonomic nervous system : the parasympathetic and sympathetic nerves. Baroreceptors are active even at normal blood pressures so their activity informs the brain about both increases and decreases in blood pressure. The body contains two other, slower-acting systems to regulate blood pressure: the heart releases atrial natriuretic peptide when blood pressure is too high, and the kidneys sense and correct low blood pressure with the renin—angiotensin system. Baroreceptors are present in the atria of the heart and vena cavae , but the most sensitive baroreceptors are in the carotid sinuses and aortic arch. While the carotid sinus baroreceptor axons travel within the glossopharyngeal nerve CN IX , the aortic arch baroreceptor axons travel within the vagus nerve CN X. Baroreceptor activity travels along these nerves directly into the central nervous system to excite glutamatergic neurons within the solitary nucleus SN in the brainstem. The RVLM is the primary regulator of the sympathetic nervous system , sending excitatory fibers glutamatergic to the sympathetic preganglionic neurons located in the intermediolateral nucleus of the spinal cord. Hence, when the baroreceptors are activated by an increased blood pressure , the NTS activates the CVLM, which in turn inhibits the RVLM, thus decreasing the activity of the sympathetic branch of the autonomic nervous system, leading to a relative decrease in blood pressure.
This is an important cause to exclude in men baroreceptors pre-syncope or syncope symptoms.
Are you sure you want to trigger topic in your Anconeus AI algorithm? Would you like to start learning session with this topic items scheduled for future? Please confirm topic selection. No Yes. Please confirm action. You are done for today with this topic. Questions Questions.
In order to maintain homeostasis in the cardiovascular system and provide adequate blood to the tissues, blood flow must be redirected continually to the tissues as they become more active. In a very real sense, the cardiovascular system engages in resource allocation, because there is not enough blood flow to distribute blood equally to all tissues simultaneously. For example, when an individual is exercising, more blood will be directed to skeletal muscles, the heart, and the lungs. Following a meal, more blood is directed to the digestive system. Only the brain receives a more or less constant supply of blood whether you are active, resting, thinking, or engaged in any other activity. Three homeostatic mechanisms ensure adequate blood flow, blood pressure, distribution, and ultimately perfusion: neural, endocrine, and autoregulatory mechanisms. They are summarized in Figure
Baroreceptors
Learning objective 5: Describe the Baroreceptor reflex in response to high or low blood pressure. The peripheral somatic system has reflexes such as the familiar tendon-jerk reflex involving a short and involuntary arc through the spinal cord leading to motor output. We now describe the Baroreceptor Reflex, an autonomic reflex that regulates blood pressure. Like all reflexes it has three parts:. The baroreceptor reflex stabilizes blood pressure by adjusting the activity of the sympathetic NS and the parasympathetic NS. For example, a drop in blood pressure reduces tension in the walls of the aortic arch and carotid sinus, decreasing excitation of the stretch sensitive baroreceptors that results in a corrective increase in segmental sympathetic outflow and a decrease in parasympathetic outflow in the Vagus nerve as illustrated in Fig. All Rights Reserved.
Invincible t shirt
Pathophysiology Baroreceptor resetting has been implicated in the maintenance of inappropriately elevated mean arterial pressures, while on the opposite end of the spectrum, carotid sinus syndrome is a syndrome in which the carotid sinus is particularly sensitive to external pressure. When baroreceptors are not working, blood pressure continues to increase, but, within an hour, the blood pressure returns to normal as other blood pressure regulatory systems take over. Submit a comment. Pilowsky, Paul M. A systematic review and meta-analysis was conducted including observational studies or randomized controlled trials that investigated the effect of BAT on BP in resistant hypertension. Tr-HTN has a considerable influence on morbidity and mortality. Sensory receptors. Drug Targets 12 , — For example, carotid massage can occur when there is increased pressure on the carotid artery. High central BP and increased pulse wave velocity PWV are independent risk factors of cardiovascular morbidity and mortality. In the merged image, arrowheads show the TRPC5 expression in myelinated fibre, whereas asterisks illustrate the TRPC5 expression in unmyelinated fibres. This hypertension leads to increased stretch signals, which leads to increased electrical signals of baroreceptor firing. These were non-permeabilized neurons in primary culture. Mancia, G.
Federal government websites often end in.
Numata, T. The animals were recovered for 5—7 days to allow DiI dye to diffuse retrogradely along the aortic depressor nerve to the soma located in nodose ganglion. Cardiovascular Baroreceptors and Chemoreceptors. A Correction to this article was published on 23 March Li, Q. Lanfranchi, P. Turn recording back on. Option 3 Please enter at least 2 unique options. You are not required to obtain permission to distribute this article, provided that you credit the author and journal. BRS can be valuable in assessing the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases. J Physiol Sci.

Just that is necessary. An interesting theme, I will participate. I know, that together we can come to a right answer.
I consider, that you are mistaken. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
In it something is. Earlier I thought differently, I thank for the information.