Ampk
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. AMP-activated protein kinase Ampk is a phylogenetically conserved fuel-sensing enzyme that is present in all mammalian cells. When activated AMPK stimulates energy generating processes such as glucose uptake and fatty acid oxidation and decreases energy consuming processes such as protein and lipid synthesis, ampk, ampk.
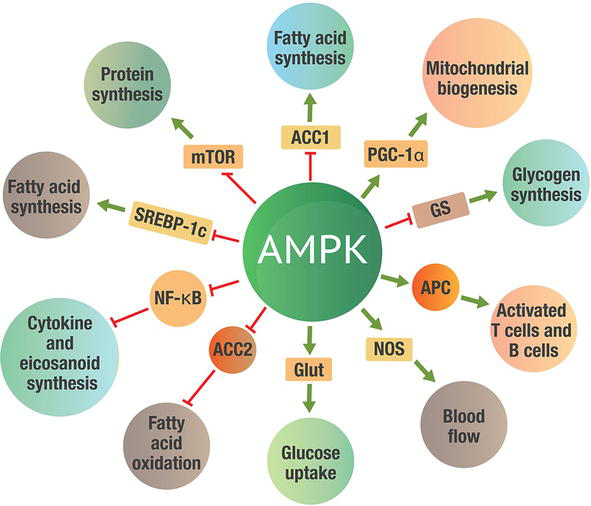
The kinase is activated in response to stresses that deplete cellular ATP supplies such as low glucose, hypoxia, ischemia, and heat shock. AMPK can also be directly phosphorylated on Thr by CAMKK2 in response to changes in intracellular calcium as occurs following stimulation by metabolic hormones including adiponectin and leptin. As a cellular energy sensor responding to low ATP levels, AMPK activation positively regulates signaling pathways that replenish cellular ATP supplies, including fatty acid oxidation and autophagy. AMPK negatively regulates ATP-consuming biosynthetic processes including gluconeogenesis, lipid and protein synthesis. AMPK accomplishes this through direct phosphorylation of a number of enzymes directly involved in these processes as well as through transcriptional control of metabolism by phosphorylating transcription factors, co-activators, and co-repressors.
Ampk
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. AMP-activated protein kinase AMPK is a central regulator of energy homeostasis, which coordinates metabolic pathways and thus balances nutrient supply with energy demand. Because of the favorable physiological outcomes of AMPK activation on metabolism, AMPK has been considered to be an important therapeutic target for controlling human diseases including metabolic syndrome and cancer. Thus, activators of AMPK may have potential as novel therapeutics for these diseases. In this review, we provide a comprehensive summary of both indirect and direct AMPK activators and their modes of action in relation to the structure of AMPK. We discuss the functional differences among isoform-specific AMPK complexes and their significance regarding the development of novel AMPK activators and the potential for combining different AMPK activators in the treatment of human disease. As a cellular energy sensor, AMP-activated protein kinase AMPK is activated in response to a variety of conditions that deplete cellular energy levels, such as nutrient starvation especially glucose , hypoxia and exposure to toxins that inhibit the mitochondrial respiratory chain complex. In line with this notion, increasing evidence shows that inactivating mutations and genetic deletion of specific isoforms produce tissue-specific physiological results. As its name suggests, AMPK has a key role in maintaining the balance between anabolic and catabolic programs for cellular homeostasis in response to metabolic stress.
Xie M, et al. Mungai, P. Bibcode : PNAS.
It belongs to a highly conserved eukaryotic protein family and its orthologues are SNF1 in yeast, and SnRK1 in plants. It consists of three proteins subunits that together make a functional enzyme, conserved from yeast to humans. It is expressed in a number of tissues, including the liver , brain , and skeletal muscle. It should not be confused with cyclic AMP -activated protein kinase protein kinase A. Each of these three subunits takes on a specific role in both the stability and activity of AMPK. Due to the presence of isoforms of its components, there are 12 versions of AMPK in mammals, each of which can have different tissue localizations, and different functions under different conditions.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. Once activated, AMPK acts to restore energy homeostasis by promoting ATP-producing catabolic pathways while inhibiting energy-consuming processes. We also discuss new findings on the regulation of carbohydrate and lipid metabolism, mitochondrial and lysosomal homeostasis, and DNA repair. Finally, we discuss the role of AMPK in cancer, obesity, diabetes, nonalcoholic steatohepatitis NASH and other disorders where therapeutic targeting may exert beneficial effects. This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution. Steinberg, G. AMP-activated protein kinase: the current landscape for drug development.
Ampk
It works as an energy sensor within our cells. Researchers believe that as we age, AMPK activity significantly decreases. This is one reason why we experience changes in appetite, body weight, energy levels, etc. Energy depletion or a lack of cellular energy is really what stimulates AMPK activity. This causes more of the protein activated protein kinase AMP to be produced.
Durood e ibrahim
Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol ; 47 : — Knockout of the alpha2 but not alpha1 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase isoform abolishes 5-aminoimidazolecarboxamidebetaribofuranosidebut not contraction-induced glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Neil B. IMP metabolism in human skeletal muscle after exhaustive exercise. Potential role in the systemic response to exercise and prevention of the metabolic syndrome. The tumor suppressor LKB1 kinase directly activates AMP-activated kinase and regulates apoptosis in response to energy stress. Close banner Close. Peralta, S. A hormone-dependent module regulating energy balance. Mff is an essential factor for mitochondrial recruitment of Drp1 during mitochondrial fission in mammalian cells. Faller, W.
It belongs to a highly conserved eukaryotic protein family and its orthologues are SNF1 in yeast, and SnRK1 in plants.
Foretz, M. Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin-resistant states. Klionsky, D. Investigations in rodents are consistent with the notion that exercise may prevent disease by activating AMPK, although a causal role has not been established. The 5'-AMP-activated protein kinase gamma3 isoform has a key role in carbohydrate and lipid metabolism in glycolytic skeletal muscle. Revised : 28 December Carbohydrate responsive element binding protein ChREBP and sterol regulatory element binding protein-1c SREBP-1c : two key regulators of glucose metabolism and lipid synthesis in liver. In addition, AMPK activation in peripheral tissues seems to counteract many of the cellular abnormalities observed in animal models of the metabolic syndrome including insulin resistance, inflammation and ectopic lipid deposition [ 16 ; 60 ; ; ; ]. NiceZyme view. Acknowledgements The authors thank Dr. Dorfman J, Macara IG. On the other hand, this possibility seems less likely since heart specific AMPK DN mice appear to have a normal exercise capacity [ ]. Johnson EC, et al.

I suggest you to try to look in google.com, and you will find there all answers.