Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration gained by an object due to gravitational force. Acceleration due to gravity is represented by g. The standard value of g on the surface of the earth at sea level is 9. Gravity is the force with which the earth attracts a body towards its centre.
In this article, you will learn about acceleration due to gravity problems and acceleration due to the gravity formula. We have all witnessed gravity in action at some point in our lives. After all, it is the power that keeps our feet firmly planted on the earth. If we throw a ball in the air in an upward motion. It will then fall on its own. When the ball is moving upwards, its speed will be slower than when it is moving downwards.
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
.
Does mass have any effect on acceleration due to gravity?
.
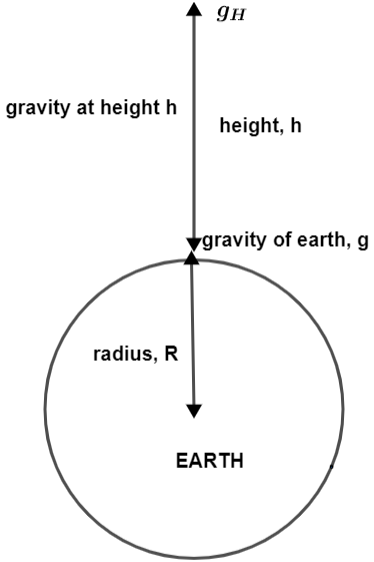
Variation of g with height and depth : Acceleration due to gravity or g varies as the height or depth varies with respect to the surface of the earth. This is known as the variation of g with height and depth. R is the radius of the earth. This also means the value of g is maximum on the surface of the earth itself. Now, to discuss exactly how acceleration due to gravity changes with height and depth with respect to the surface of the earth, we will take the help of simple mathematics and analyze separately 1 the Variation of g with height and 2 the Variation of g with depth and derive the formulas describing this variation of g with altitude and depth. This is the formula for g at height h.
Acceleration due to gravity at a height h
Take something in your hand and toss it down. Its speed is zero when you free it from your grip. Its pace rises as it descends. It flies faster the longer it goes. This sounds like acceleration. Acceleration, on the other hand, implies more than just rising speed. Pick up the same object and throw it into the air vertically. It will slow down on the way up until it comes to a halt and reverses course. Acceleration may also be described as a decrease in speed.
Noob de roblox
Where M is the mass of the earth, and R is the radius of the earth. Conclusion When falling freely under the influence of gravity at the same point on the Earth, all things, regardless of mass, experience the same acceleration g. Consider a test mass m at a height h from the surface of the earth. In this article, you will learn about acceleration due to gravity problems and acceleration due to the gravity formula. Ans : Unless air resistance impacts one thing more than another, all falling o The acceleration due to gravity at depth h is given by g2, while the radius of the earth is given by R. It can be used as a voltage regulator. Acceleration due to gravity is the acceleration gained by an object due to gravitational force. View Result. Subscribe Now. So if a person moves from the equator to the poles, their weight decreases as the value of g decreases.
The numerical value of g is 9. There are slight variations of this value depending on a few factors.
Let us consider two bodies of masses, m a and m b. When falling freely under the influence of gravity at the same point on the Earth, all things, regardless of mass, experience the same acceleration g. Learn about the zeroth law definitions and their examples. What are some examples of acceleration due to gravity? The radius of the earth is R. According to the principle of equivalence, the inertial mass and gravitational mass are identical. Does gravity have acceleration? Allotment of Examination Centre. What are the three factors that create acceleration? Access free live classes and tests on the app. From the above equation, it is clear that acceleration due to gravity is more at the poles and less at the equator.

0 thoughts on “Acceleration due to gravity at a height h”