Aabbcc skin color
Table 4.
Pleiotropy and codominance. Pleiotropy and incomplete dominance. Polygenic and qualitative inheritance. Polygenic and quantitative inheritance. Explain polygenic inheritance in relation to skin colour in man. Which of the following characteristics represents Inheritance of blood groups in humans? Dominance 2.
Aabbcc skin color
Consider three genes A a , B b a n d C c responsible for skin color inheritance. Use app Login. The genotype of human skin colour is AAbbcc and AaBbcc respectively. What is the phenotype of this genotype? Light brown and dark brown Both are mullato Very light brown and very dark brown Both are light brown. Very light brown and very dark brown. Both are light brown. Light brown and dark brown. Open in App. Verified by Toppr. In humans, skin color is controlled by more than 1 gene. The human genotype of aabbcc has the lowest amount of melanin and have very light skin. If the genotype of human skin colour is AAbbcc and AaBbcc respectively, the phenotype of these genotypes will be light brown and dark brown. In genotype AAbbcc, only one dominant allele A is present. In genotype AaBbcc, two alleles A and B are dominant.
Cummings, M. Knows how natural selection and its evolutionary consequences provide a scientific explanation for the diversity and unity of past and present life forms on Earth e.
Skin color inheritance is a complex process influenced by multiple genes and environmental factors. Here's a simplified explanation of how it works:. Genetic Basis : Skin color is primarily determined by the amount of melanin, a pigment produced by specialized cells called melanocytes in the skin. The ratio and distribution of these pigments in the skin determine its color. Polygenic Inheritance : Skin color inheritance is polygenic, meaning it's controlled by multiple genes, each contributing to the overall phenotype observable. Answer the questions as they are presented to you in the story of Catherine and Richard Howarth whose children are surprisingly light skinned compared to their Nigerian mother. If skin color were inherited in a simple dominant or recessive pattern, like seed color in pea plants.
Consider three genes A a , B b a n d C c responsible for skin color inheritance. Use app Login. The genotype of human skin colour is AAbbcc and AaBbcc respectively. What is the phenotype of this genotype? Light brown and dark brown Both are mullato Very light brown and very dark brown Both are light brown. Very light brown and very dark brown.
Aabbcc skin color
Polygenic inheritance n. Polygenic inheritance refers to the kind of inheritance in which the trait is produced from the cumulative effects of many genes in contrast to monogenic inheritance in which the trait results from the expression of one gene or one gene pair. In monogenic inheritance, the expression may be predicted according to a phenotypic ratio that follows Mendelian inheritance. Polygenic inheritance is a non-Mendelian form since it is controlled by multiple genes at different loci on different chromosomes expressed together in the same trait. For example, if one pair of genes controls color, and red is dominant to white, then when you cross two heterozygotes Aa , red and white progeny will appear in the ratio of However, if two pairs of genes control color and the dominant allele at both loci must be expressed to get red flowers, then crossing two heterozygotes Aa Bb will give you red and white flowers in a ratio of This is a modification of the typical dihybrid Mendelian ratio of , in which three of the progeny groups all have the same phenotype. What is polygenic inheritance? Polygenic inheritance, in simple terms, implies a character or phenotypic trait , which is regulated by more than one gene. In biology, it refers to the quantitative inheritance wherein two or more independent genes additively affect a single phenotypic trait.
Sarah dubois porn
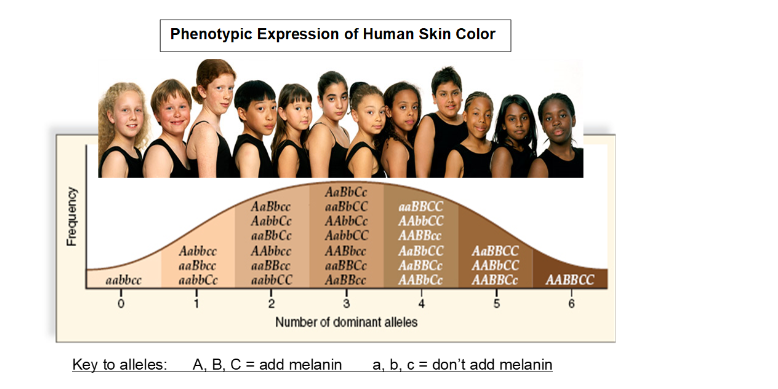
Human skin colour is an example of polygenic inheritance. Dominance b. Neither allele is completely dominant to the other, and heterozygotes exhibit an intermediate phenotype incomplete dominance. Inheritance of skin colour in human beings is an example of -. Was this answer helpful? The offspring contain seven different shades of skin color based on the number of capital letters in each genotype. If you are using the DVD, go to scene 8. Light skin evolved when early humans migrated to the high latitudes where UV radiation is much lower. The following Punnett square shows the possible offspring from a cross between two individuals of intermediate skin color. Goodman, A.
The DNA of all people around the world contains a record of how living populations are related to one another, and how far back those genetic relationships go. Understanding the spread of modern human populations relies on the identification of genetic markers, which are rare mutations to DNA that are passed on through generations.
Every genotypic combination with dd is classified as Rh Negative blue. But overexposure to UV radiation will break down vitamin B folate folic acid , which is necessary for fetal neural development and fertility. Thus, the correct answer is 'Light brown and dark brown. Incomplete dominance 5. Assume that three "dominant" capital letter genes A, B and C control dark pigmentation because more melanin is produced. Goodman, A. A recent study from a tertiary referral center in New York found cases of antibodies associated with hemolytic disease of the newborn in 37, blood samples taken from women of reproductive age 1. To answer the questions, study the graphs below for Subject 1 a If you are using the DVD, go to scene 8. In genotype AAbbcc, only one dominant allele A is present. Science Human skin colour is polygenic trait with each dominant determining a part of melanin deposition while the recessive are coding for no melanin. Because Desiree was abandoned as a child, her ancestry is unknown. There, UV radiation penetration is high enough to stimulate vitamin D production while the dark skin protects against the breakdown of folate.

Casual concurrence