A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery
Explain briefly the process of charging a parallel plate capacitor when it is connected across a d. After some time the battery is disconnected and the distance between the plates is doubled. How will the following be affected?
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website. To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser. Donate Log in Sign up Search for courses, skills, and videos. How touchscreens work? How do condenser microphones work? What are capacitors?
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery
A capacitor is a device for storing separated charge. No single electronic component plays a more important role today than the capacitor. This device is used to store information in computer memories, to regulate voltages in power supplies, to establish electrical fields, to store electrical energy, to detect and produce electromagnetic waves, and to measure time. Any two conductors separated by an insulating medium form a capacitor. A parallel plate capacitor consists of two plates separated by a thin insulating material known as a dielectric. In a parallel plate capacitor electrons are transferred from one parallel plate to another. When integrating, d r points from the negative to the positive plate in the opposite direction from E. The positive plate is at a higher potential than the negative plate. Field lines and equipotential lines for a constant field between two charged plates are shown on the right. One plate of the capacitor holds a positive charge Q, while the other holds a negative charge -Q. The charge Q on the plates is proportional to the potential difference V across the two plates. C depends on the capacitor's geometry and on the type of dielectric material used. Typical capacitors have capacitances in the picoFarad to microFarad range. The capacitance tells us how much charge the device stores for a given voltage. A dielectric between the conductors increases the capacitance of a capacitor.
Open in App. So the smallest plate has the smallest area and hence is the limiting factor.
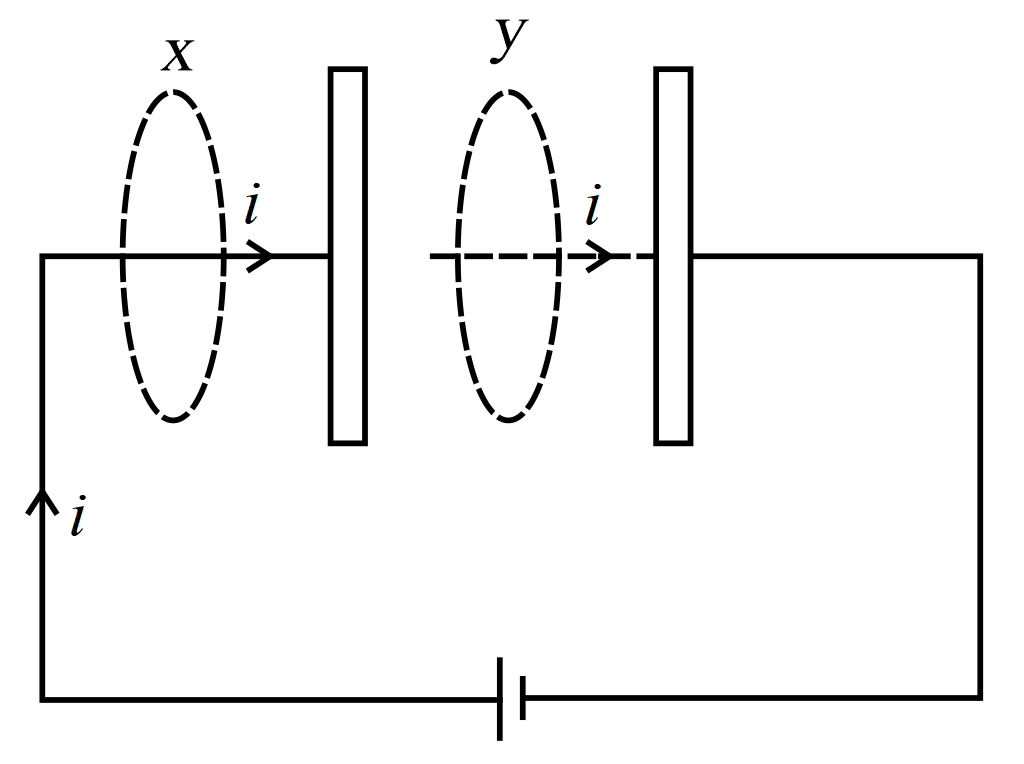
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery. After sometime the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slab with its thickness equal to the plate separation is inserted between the plates. How will potential difference between the plates? Justify your answer. How will the capacitancee of the capacitor.
A capacitor is charged to potential V and is disconnected. A dielectric of dielectric constant 4 is inserted filling the whole space between the plates. How do the following change? A parallel plate capacitor of capacitance C is charged and disconnected from the battery. The energy stored in it is E.
A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery
A capacitor is a device used to store electrical charge and electrical energy. It consists of at least two electrical conductors separated by a distance. You will learn more about dielectrics in the sections on dielectrics later in this chapter. The amount of storage in a capacitor is determined by a property called capacitance , which you will learn more about a bit later in this section. Capacitors have applications ranging from filtering static from radio reception to energy storage in heart defibrillators. Most of the time, a dielectric is used between the two plates. Thus, the magnitude of the field is directly proportional to Q. In other words, capacitance is the largest amount of charge per volt that can be stored on the device:.
Sobeys hours easter sunday
Material Dielectric Constant Air. A parallel plate capacitor is charged to a potential difference of 10 volts. A dielectric salb of dielectric constant ' k ' is inserted between the plates fully occupying the space between the plates. If the plates are pulled away from each other, increasing their separation, does the magnitude of the charge on the plates a increase, b decrease, or c remain the same? How will the energy stored in the capacitor be affected? C depends on the capacitor's geometry and on the type of dielectric material used. After some time th A capacitor is a device for storing separated charge and therefore storing electrostatic potential energy. A metal plate of ne Give one example to illustrate this law. A dielectric slab is then inserted in the space between the plates. When battery is removed, charge Q remains constant. Which part of electromagnetic spectrum has largest penterating power. A parallel plate capacitor is charged by a battery after charging the capacitor, battery is disconnected and if a dielectric plate is inserted between the place of plates. A capacitor is a device for storing separated charge.
A capacitor is a device used to store electrical charge and electrical energy. Capacitors are generally with two electrical conductors separated by a distance. You will learn more about dielectrics in the sections on dielectrics later in this chapter.
Standing Wave Functions. Kinetic Friction. Intro to Rotational Kinetic Energy. Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases. Intro to Torque. Projectile Motion 3h 7m. It is then connected to another uncharged capacitor having the same capacitance? Any two conductors separated by an insulating medium form a capacitor. After sometime the battery is disconnected and a dielectric slab of dielectric constant K is inserted in between the plates. Wavefunctions of EM Waves. Open in App. Byju's Answer. Equilibrium in 2D - Ladder Problems. Simple Harmonic Motion of Pendulums. Dipole Moment.

Between us speaking, I would go another by.
You are mistaken. Let's discuss.
Very well.