50s ribosomal subunit
Bacteria harbor a number GTPases that function in the assembly of the ribosome and are essential for growth. Homologs of this protein are also implicated in 50s ribosomal subunit assembly of the large subunit of the mitochondrial and eukaryotic ribosome.
Thank you for visiting nature. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer. In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript. We have calculated at 5. More than base pairs of A-form RNA duplex have been fitted into this map, as have regions of non-A-form duplex, single-stranded segments and tetraloops. The long rods of RNA crisscrossing the subunit arise from the stacking of short, separate double helices, not all of which are A-form, and in many places proteins crosslink two or more of these rods.
50s ribosomal subunit
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Despite the identification of many factors that facilitate ribosome assembly, the molecular mechanisms by which they drive ribosome biogenesis are poorly understood. Here, we analyze the late stages of assembly of the 50S subunit using Bacillus subtilis cells depleted of RbgA, a highly conserved GTPase. We found that RbgA-depleted cells accumulate late assembly intermediates bearing sub-stoichiometric quantities of ribosomal proteins L16, L27, L28, L33a, L35 and L Cryo-electron microscopy and chemical probing revealed that the central protuberance, the GTPase associating region and tRNA-binding sites in this intermediate are unstructured. These findings demonstrate that key functional sites of the 50S subunit remain unstructured until late stages of maturation, preventing the incomplete subunit from prematurely engaging in translation. Finally, structural and biochemical analysis of a ribosome particle depleted of L16 indicate that L16 binding is necessary for the stimulation of RbgA GTPase activity and, in turn, release of this co-factor, and for conversion of the intermediate to a complete 50S subunit. In bacteria, ribosome biogenesis requires the synthesis, folding, chemical modification and assembly of 3 large RNAs and 55 proteins. This complex process is completed rapidly and efficiently with bacterial cells synthesizing up to 50 ribosomes per generation 1. Several decades ago, the groups of Nomura 2—4 and Nierhaus 5 , 6 determined the thermodynamic binding dependencies for ribosomal proteins r-proteins in the 30S and 50S bacterial subunits and used these data to reconstruct assembly maps depicting r-protein binding.
The mechanism for activation of GTP hydrolysis on the ribosome.
The structures of ribosomal proteins and their interactions with RNA have been examined in the refined crystal structure of the Haloarcula marismortui large ribosomal subunit. The protein structures fall into six groups based on their topology. The 50S subunit proteins function primarily to stabilize inter-domain interactions that are necessary to maintain the subunit's structural integrity. An extraordinary variety of protein-RNA interactions is observed. Electrostatic interactions between numerous arginine and lysine residues, particularly those in tail extensions, and the phosphate groups of the RNA backbone mediate many protein-RNA contacts.
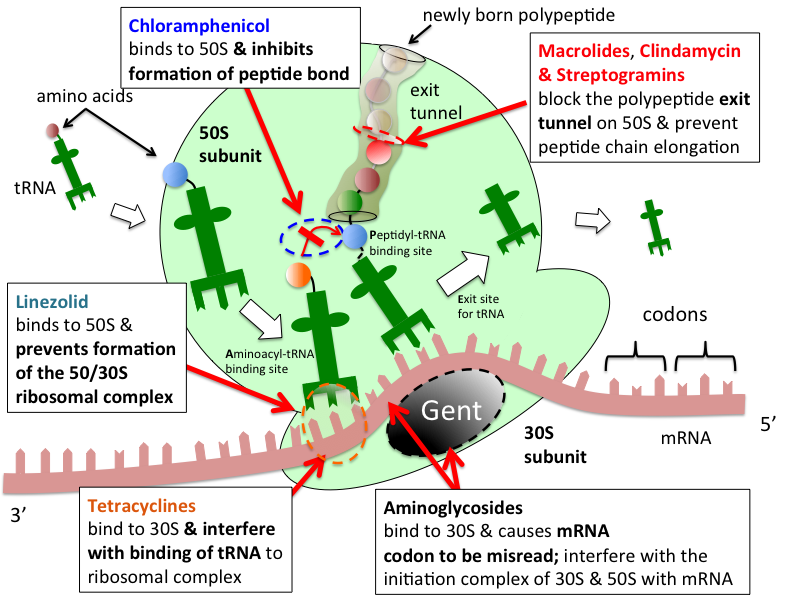
It is the site of inhibition for antibiotics such as macrolides , chloramphenicol , clindamycin , and the pleuromutilins. Despite having the same sedimentation rate, bacterial and archaeal ribosomes can be quite different. X-ray crystallography has yielded electron density maps allowing the structure of the 50S in Haloarcula marismortui archaeon to be determined to 2. The secondary structure of 23S is divided into six large domains, within which domain V is most important in its peptidyl transferase [3] activity. Each domain contains normal secondary structure e. At tertiary structure level, the large subunit rRNA is a single gigantic domain while the small subunit contains three structural domains. This difference reflects the lesser flexibility of the large subunit required by its function.
50s ribosomal subunit
Ribosomes are composed of two subunits with densities of 50S and 30S "S" refers to a unit of density called the Svedberg unit. The two subunits combine during protein synthesis to form a complete 70S ribosome about 25nm in diameter. A typical bacterium may have as many as 15, ribosomes.
Spiderman face sketch
Simons, R. Ero, R. We are also thankful to Richard Fekete for suggestions about the primer extension method. RbgA was segmented and computationally removed for easy visualization of the A, P and E sites. Methods used in the structural determination of bovine mitochondrial F1 ATPase. Alternatively, it is also possible that, like BipA, the expression of rplT increases to promote and adjust 50S ribosomal subunit assembly under cold-shock stress conditions. Vitrification of the specimen was performed in a Vitrobot FEI by blotting the grids twice, 7 s each time, before they were plunged into liquid ethane. In this study, to demonstrate the role of BipA in the 50S ribosomal subunit and possibly to find an interplaying partner s , a genomic library was constructed and suppressor screening was conducted. Landmarks of the 50S structure including the CP, and L1 stalk are indicated. Sign In or Create an Account. Open in a separate window. This reaction was studied by cryo-EM and single particle analysis.
Federal government websites often end in. The site is secure. Ribosomes are among the largest and most dynamic molecular motors.
Your comment will be reviewed and published at the journal's discretion. Among them, we identified the rplT gene as partially recovering cold-sensitive growth and ribosome defects observed in the bipA -deleted strain. About this article Cite this article Ban, N. Suppressive activities of truncated mutant forms of L Mueller A. D 53 , — Barrientos A. Quality control mechanisms during ribosome maturation. Fractions corresponding to ribosomal subunits of interest were pooled and pelleted by centrifugation for 16 h at g in a Beckman MLA rotor. Wimberly, B. This chaperone activity was independent of nucleotide and GTP hydrolysis activity Choi and Hwang,

0 thoughts on “50s ribosomal subunit”