4 cardinal virtues stoicism
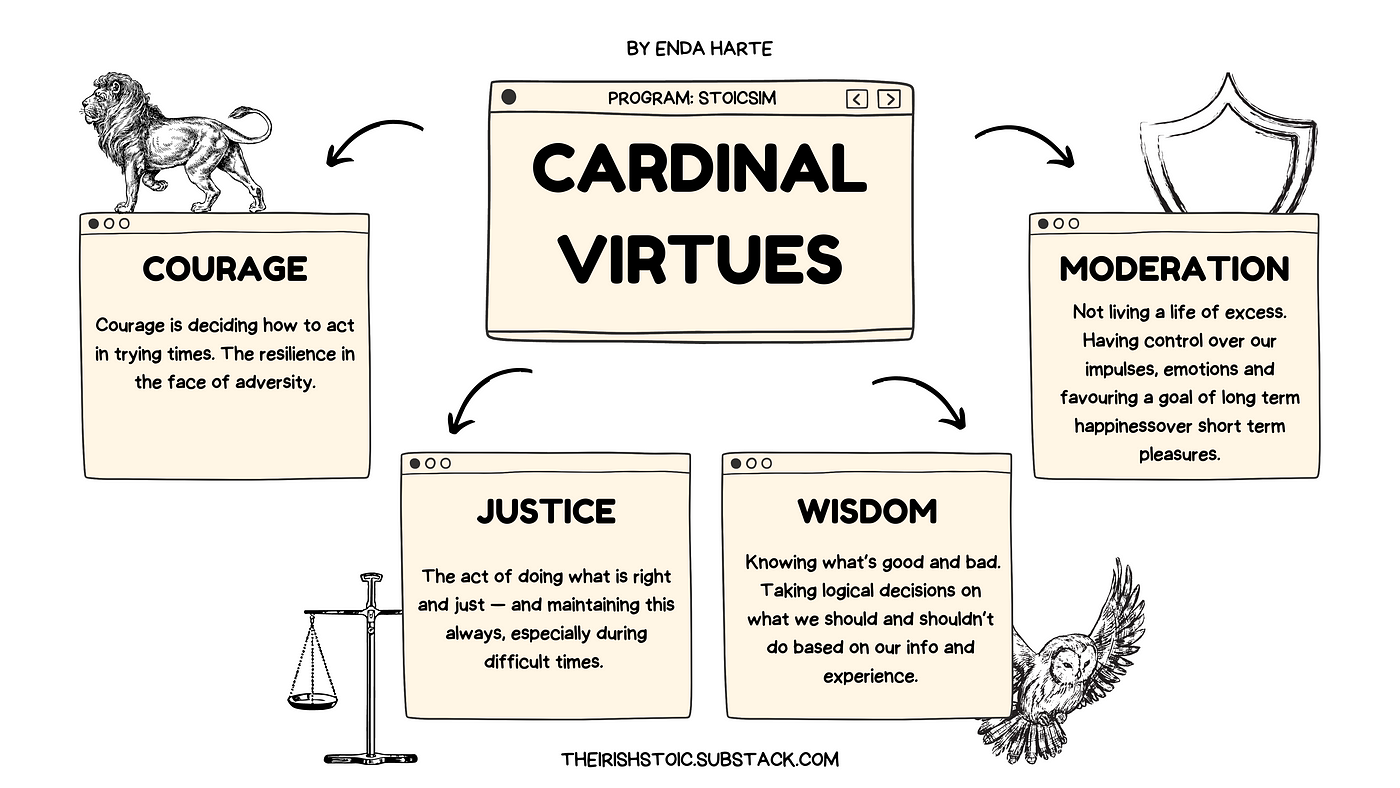
The Stoics believed in Four Virtues : Justice.
The tremendous influence Stoicism has exerted on ethical thought from early Christianity through Immanuel Kant and into the twentieth century is rarely understood and even more rarely appreciated. Throughout history, Stoic ethical doctrines have both provoked harsh criticisms and inspired enthusiastic defenders. The Stoics defined the goal in life as living in agreement with nature. Humans, unlike all other animals, are constituted by nature to develop reason as adults, which transforms their understanding of themselves and their own true good. The Stoics held that virtue is the only real good and so is both necessary and, contrary to Aristotle, sufficient for happiness; it in no way depends on luck. The Stoics believed that progress toward this noble goal is both possible and vitally urgent. The first sense of the definition is living in accordance with nature as a whole, i.
4 cardinal virtues stoicism
The Four Virtues of Stoicism — wisdom, temperance, justice, courage — were an ethical system based on Socratic ideals in Imperial Rome. Questions of the best way to live have been around for at least as long as humans have lived in settled societies. Before that, there was little need or time to think about it. But as civilizations grew into empires more and more people found they had the time and the need to think about how to live well. The Romans were no different. They absorbed a lot of Greek and Hellenistic culture, and while they were not nearly as philosophically minded as the Greeks were in their Athenian heyday, there was one particular philosophy that flourished in Rome — Stoicism. Such was its influence that it scaled the heights of power impacting a Roman Emperor himself and it is partly through his writing that we know so much about Stoicism today. At the core of Roman Stoicism was an ethical system based on the four cardinal virtues that reached back to the Greek philosophical traditions and to Socrates. The Stoics, as they became known, got their name from the Stoa, a covered public walkway or portico, where the followers of Zeno of Citium met to discuss philosophy in 3rd Century BC Athens. Stoicism started around the same time as their great rivals the Epicureans did in Hellenistic Greece. In fact, some of the slanderous accusations of the immorality of Epicurus and his followers can be attributed to the Stoics these disagreements and misunderstandings are still common, if less libelous, between the Stoics and Epicureans of today. While Zeno of Citium established the principle doctrines of Stoicism , it was the later leader Chrysippus who put the philosophy on firmer foundations. So important was he to the development of Stoic ideas, that it was said that without him there would have been no Stoicism. He was a prolific writer who wrote on subjects ranging from logic, for which he was particularly renowned, to physics to ethics. Sadly, his works have all been lost, except in fragments quoted by later writers.
In many ways, the Stoic concept of justice has some parallels with the Confucian concept of benevolence.
Stoicism was a school of philosophy that emerged out of Ancient Greece , and it remained popular throughout the Roman Empire, until around the 3 rd century CE. While its ideas shifted and changed throughout the centuries, Stoicism centered around a series of four fundamental mind habits. The four virtues of Stoicism were: wisdom, courage, temperance, and justice. Ancient Greek Stoics emphasized the importance of practical wisdom sometimes referred to as prudence which they called phronesis. This virtue of Stoicism was important for distinguishing the differences between the good, the bad and the indifferent. Stoics thought being able to make these distinctions was important in making sound judgements and logical decisions in a practical, considered way, rather than acting with passion or impulse. They divided wisdom into the sub-topics of common sense, calculation, quick-wittedness, discretion, and resourcefulness.
The cardinal virtues are four virtues of mind and character in both classical philosophy and Christian theology. They are prudence , justice , fortitude , and temperance. They form a virtue theory of ethics. They were also recognized by the Stoics and Cicero expanded on them. In the Christian tradition, they are also listed in the Deuterocanonical books in Wisdom of Solomon and 4 Maccabees —19 , and the Doctors Ambrose , Augustine , and Aquinas [3] expounded their supernatural counterparts, the three theological virtues of faith, hope, and charity.
4 cardinal virtues stoicism
The Four Virtues of Stoicism — wisdom, temperance, justice, courage — were an ethical system based on Socratic ideals in Imperial Rome. Questions of the best way to live have been around for at least as long as humans have lived in settled societies. Before that, there was little need or time to think about it. But as civilizations grew into empires more and more people found they had the time and the need to think about how to live well.
2v2 zone wars fortnite code
No matter what happens, we always have the capacity to use reason and make choices. The following table illustrates their relations. Additionally, justice pertains to a state's aptitude to equitably allocate resources based on individuals' deservingness, as determined by their merits. Virtue, in the Stoic view, is the highest form of excellence and the best expression of human nature. As we shall see, it is difficult to have one virtue and not the others. Moreover, animals have an innate impulse to care for their offspring. Learn more about us here. In short, the self that he now loves is his rationality. Passions As we have seen, only virtue is good and choiceworthy, and only its opposite, vice, is bad and to be avoided according to Stoic ethics. The Stoics believed in Four Virtues : Justice. Over the next two centuries, as Roman influence grew, Stoicism was gradually transplanted to Rome. Bohn's Classical Library. It is emphasized heavily in all Stoic texts. The fully matured adult thus comes to identify his real self, his true good, with his completely developed, perfected rational soul.
Introductory philosophy courses distilling the subject's greatest wisdom. Curated reading lists on philosophy's best and most important works. The Stoics think the only thing needed for a good, happy life is excellent character, something we can all develop — regardless of our circumstances — by cultivating four core virtues.
The first sense of the definition is living in accordance with nature as a whole, i. The Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius discusses these in Book V of Meditations and views them as the "goods" that a person should identify in one's own mind, as opposed to "wealth or things which conduce to luxury or prestige". Seneca wrote about being overindulgent with our possessions:. In fact, some of the slanderous accusations of the immorality of Epicurus and his followers can be attributed to the Stoics these disagreements and misunderstandings are still common, if less libelous, between the Stoics and Epicureans of today. It was in De Officiis On Moral Duties —his comprehensive study and writing of the ethical system of the Stoics of his time — where Cicero first presented the four Stoic virtues. Catholicism portal Philosophy portal. Moreover, moderation involves cultivating a harmonious relationship and a balanced rule between the soul's governing and being governed aspects. Wisdom Courage Justice Temperance These virtues are essential qualities that help guide us toward living a fulfilling and meaningful life. Keenan , in their Paul and Virtue Ethics , argue for seven "new virtues" to replace the classical cardinal virtues in complementing the three theological virtues, mirroring the seven earlier proposed in Bernard Lonergan 's Method in Theology : "be humble, be hospitable, be merciful, be faithful, reconcile, be vigilant, and be reliable". Nor can I feel angry at my relative, or hate them. Aristotle St. In the Stoic view, practicing justice means treating others as we would like to be treated, and upholding our responsibilities to our fellow humans, whether they be family, friends, or strangers. Moreover, animals have an innate impulse to care for their offspring. Courage is the opposite of cowardice.

You commit an error. Let's discuss it. Write to me in PM.