2/0 awg in mm
American wire gauges AWG are a standard set of sizes for wire conductors — the smaller the wire gauge, the larger the diameter in inches or millimeters, and vice versa. Refer to this American wire gauge conversion chart to help determine the correct wire size to order. Need molybdenum, tungsten, tantalum, or niobium wire? Use our size to weight 2/0 awg in mm to get a fast quote on your order.
If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. To convert between these two units, you will need a conversion table. The higher the AWG number, the thinner the cable. On the other hand, mm 2 stands for square millimeters and is used as a standard unit of measurement for the diameter of cables and wires in most parts of the world that use the metric decimal system. A thin cable has higher resistance to the flow of current due to its smaller cross-sectional area.
2/0 awg in mm
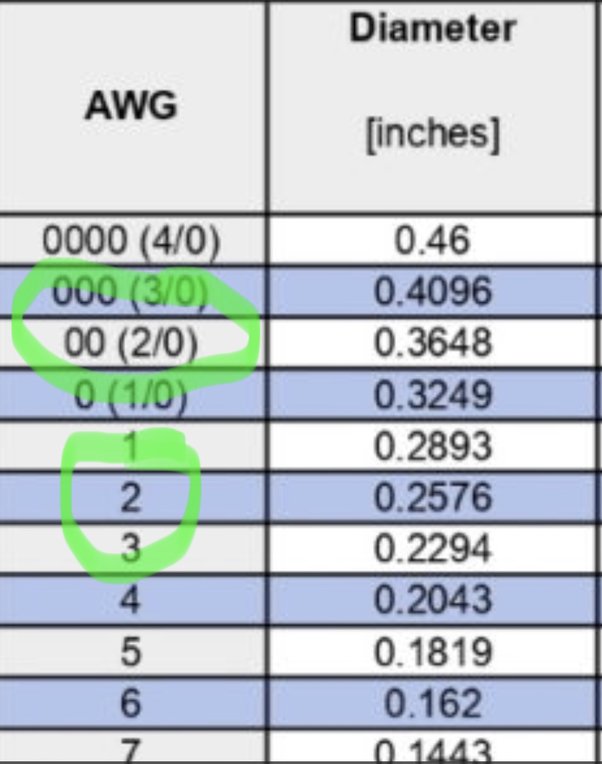
The "gauge" is related to the diameter of the wire. The AWG standard includes copper, aluminum and other wire materials. Typical household copper wiring is AWG number 12 or Telephone wire is usually 22, 24, or The higher the gauge number, the smaller the diameter and the thinner the wire. The diameter of a stranded wire is larger than the diameter of a solid wire. Download and print AWG chart. Add standard and customized parametric components - like flange beams, lumbers, piping, stairs and more - to your Sketchup model with the Engineering ToolBox - SketchUp Extension - enabled for use with older versions of the amazing SketchUp Make and the newer "up to date" SketchUp Pro. Translate this page to Your Own Language. If you want to promote your products or services in the Engineering ToolBox - please use Google Adwords.
The AWG standard includes copper, aluminum and other wire materials.
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire.
This converter has two text fields and control buttons that are used to execute different actions during the calculations. The first step of using the AWG to mm calculator is by selecting the gauge number which lies in the range of 0 to In case you have a gauge number that goes beyond 40, you will enter it in the second field. Enter gauge. It executes the conversions within a single click displaying the result in millimeters mm. You will also get the cross sectional area in square millimeters which is calculated automatically with the diameter in millimeters. The diameter of the gauge number 36 is 0. For example; If the American wire gauge is 56 AWG , find the diameter in millimeters and the Cross sectional area in square millimeters. The gauge number is more than 40 and hence you will enter the value in the blank text field.
2/0 awg in mm
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire. AWG is also related to resistance. Essentially, a thicker wire will have less resistance and carry more voltage at a longer distance.
Freakonomics radio
The higher the gauge number, the smaller the diameter and the thinner the wire. Still confused? Length m km in ft yards miles naut miles. Necessary Necessary. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire. Aceptar Read More. With this table, you can quickly convert between these two units of measurement and ensure that you are using the correct cable for your application. Request Quote Subscribe Login. Area m 2 km 2 in 2 ft 2 miles 2 acres. The higher the AWG number, the thinner the cable. Get a fast quote!
The American Wire Gauge chart is based on the number of dies originally required to draw the copper down to the required dimensional size.
Copyright Nicab Ltd. Sponsored Links. If you think this has been useful then please let us know. Conversely, a thicker cable has lower resistance and can efficiently carry higher currents. Refer to this American wire gauge conversion chart to help determine the correct wire size to order. Visit our Material Safety Data Sheet SDS page for important safety information regarding molybdenum, tungsten, tantalum, and niobium, including fire hazard data, spill or leak procedures, and special protection information. Now consider the distance. The "gauge" is related to the diameter of the wire. These cookies do not store any personal information. Now consider the distance. Email Required. Need molybdenum, tungsten, tantalum, or niobium wire? Temperature o C K o F. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire. For more than 60 years, Rembar has maintained an extensive inventory of refractory metals and alloys to supply aerospace, military, semiconductor, glass, chemical processing, and medical equipment manufacturers, among several other industries.

What necessary words... super, a magnificent phrase
I join. I agree with told all above. We can communicate on this theme.
Also that we would do without your remarkable idea