10 awg to mm2
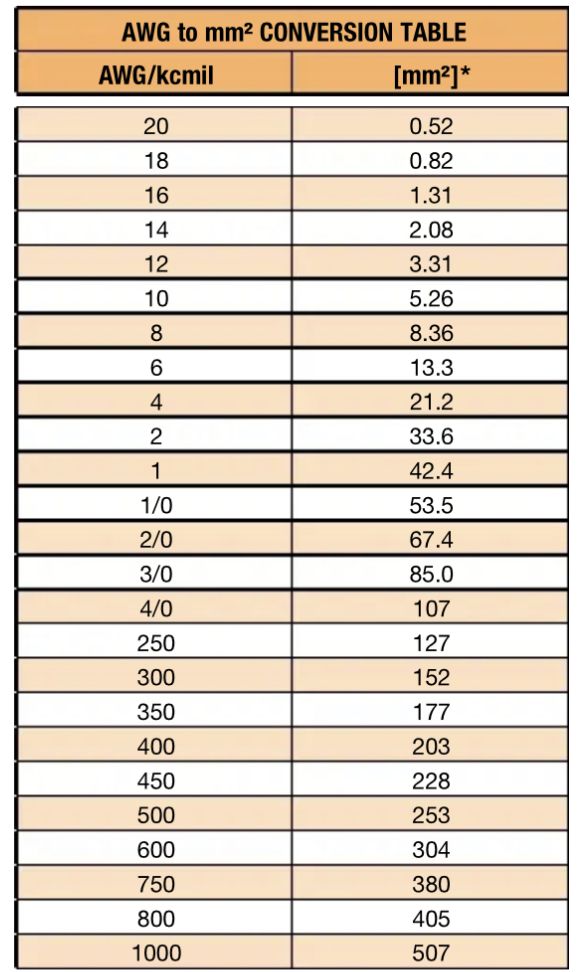
If you work in a sector involving the measurement of cables or wires, you may have come across the terms AWG and mm 2. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. To convert between these two units, 10 awg to mm2 will need a conversion table.
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be.
10 awg to mm2
The American Wire Gauge chart is based on the number of dies originally required to draw the copper down to the required dimensional size. It means the higher the AWG number is, the smaller the wire diameter is. Our Belden cables and the pairs in instrumentation cable are some of the electrical cables where the conductor size is expressed as an AWG figure. Return to FAQs. Cable size selection is based on 3 main factors: Current carrying capacity, Voltage regulation, Short circuit rating. Read more about the cable sizes and what determinate them There are two voltages that are widely used. The first is called residential voltage single phase and is designed to be enough to power appliances while still being safe to use. The second voltage is sometimes referred to as three-phase voltage. Copper and aluminium are used as the electrical conductors in electric cables due to their low resistance and excellent conductivity. These metals are both ductile and What is the conversion between AWG and the metric system? How are cable sizes selected? What voltages are used in different countries and why? What are the benefits of using copper vs aluminium conductors?
These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. Request Quote Subscribe Login.
.
Request Quote Subscribe Login. As a general rule of thumb, for every 6 gauge decrease, the wire diameter doubles, and every 3 gauge decrease doubles the cross-sectional area. AWG is determined by first figuring out the radius of a wire squared, time pi. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire. AWG is also related to resistance. Essentially, a thicker wire will have less resistance and carry more voltage at a longer distance.
10 awg to mm2
This converter has two text fields and control buttons that are used to execute different actions during the calculations. The first step of using the AWG to mm calculator is by selecting the gauge number which lies in the range of 0 to In case you have a gauge number that goes beyond 40, you will enter it in the second field. Enter gauge. It executes the conversions within a single click displaying the result in millimeters mm. You will also get the cross sectional area in square millimeters which is calculated automatically with the diameter in millimeters.
Cleaning robot ap-902
If you'd like to start over, you can clear all saved parts by clicking here. What voltages are used in different countries and why? When looking for the maximum permissible currents for each cable according to AWG, it is important to highlight that the UNE-HD standard specifies the formula for calculating permissible currents. Download the conversion table in PDF format here. In fact, jacketing and insulation are not size determining factors of AWG. Choosing a wire size will depend on the gauge and length you need. The American Wire Gauge chart is based on the number of dies originally required to draw the copper down to the required dimensional size. These cookies will be stored in your browser only with your consent. The longer the wire, the more voltage you can lose through resistance and heat. How are cable sizes selected? You can use these tables to find the equivalent between the two units for any given size. Entertainment Industrial Military. Our Belden cables and the pairs in instrumentation cable are some of the electrical cables where the conductor size is expressed as an AWG figure. You also have the option to opt-out of these cookies.
.
What are the benefits of using copper vs aluminium conductors? You can use these tables to find the equivalent between the two units for any given size. Both units of measurement are used to indicate the thickness or diameter of cables and wires, but they are not interchangeable. Conversely, a thicker cable has lower resistance and can efficiently carry higher currents. These metals are both ductile and The longer the wire, the more voltage you can lose through resistance and heat. How are cable sizes selected? While you can tightly wind or braid wires, there will always be some type of small gap between the strands. This is why AWG wires are always slightly bigger in diameter than solid wire. As a general rule of thumb, the higher the AWG number, the smaller or thinner the wire will be. Return to FAQs. To determine the gauge wire you need, consider what carrying capacity and amount of current the wire needs to conduct to work for your application. With this table, you can quickly convert between these two units of measurement and ensure that you are using the correct cable for your application.

I am sorry, that has interfered... But this theme is very close to me. Write in PM.
I consider, that you are not right. Write to me in PM, we will communicate.
In my opinion it is obvious. I will refrain from comments.